What is Decentraland (MANA)?


What is Decentraland?
Decentraland is a virtual-reality platform—a virtual world—running on the Ethereum blockchain. Users explore the project’s metaverse and populate it with content.
In Decentraland, users create various artefacts and interactive objects. Items and parcels of land in this virtual world are NFTs. They are traded on the native marketplace.
The platform uses the MANA and LAND tokens. Non-fungible LAND tokens represent parcels of land, while MANA is used for payments and governance.
The Decentraland metaverse is governed by a decentralised autonomous organisation (DAO).
Who created Decentraland, and when?
Esteban Ordano and Ariel Meilich founded Decentraland in 2015. Before that, Ordano worked as a programmer at BitPay, and Meilich as an analyst at Charles River Ventures.
Initially, the developers released a virtual world as a two-dimensional pixel map. Points were coloured and linked to metadata that enabled their identification.
In 2016, the team began building a 3D digital world.
In 2017, Decentraland raised 86,206 ETH ($24m at the time) in an ICO. The organisation maintains the project’s website and holds the intellectual-property rights. The developers kept 20% of the funds raised.
The platform’s roadmap was drawn up in 2017, and a beta version arrived in 2019. Interactive applications and in-game chat were added later.
In February 2020, the developers unveiled the metaverse’s final release.
What can you do in Decentraland?
The platform sits in the GameFi sector, offering both gaming and financial features. Players explore territories, socialise and take part in interactive scenes, and they create virtual objects as NFTs.
A range of events take place in Decentraland, including exhibitions, trainings and seminars. The metaverse can be used to advertise products and services, and to promote upcoming activities.
The project’s white paper outlines ways to expand the metaverse and its gameplay. Users can create objects, mini-games and applications. The team offers two tools to build the virtual world:
- The Builder. It is a browser-based editor that lets users create and edit metaverse content by dragging and dropping objects.
- Decentraland SDK. A development kit for building interactive scenes and custom elements.
Libraries enhance interactive content. Landowners can create mini-games and earn revenue from them.
Virtual items and land can be traded freely on Decentraland Marketplace.
What is in the Decentraland metaverse?
The virtual world spans a 300-by-300 grid of parcels. All land corresponds to non-fungible LAND tokens.
The world comprises 92,598 parcels. Each parcel covers 256 square metres (a 16m by 16m square).
A parcel’s position is defined by x and y coordinates. Owners decide what content to place on their land.
The metaverse is divided into themed districts. The concept brings like-minded users together in areas that match their interests. At the time of writing there are 39 active districts.
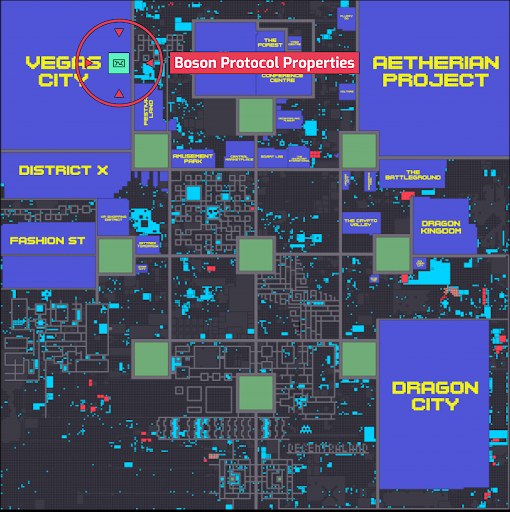
These districts have distinct features that attract visitors. The most popular include:
- Aetheria. The metaverse’s largest district, with more than 8,000 parcels. It features real estate and objects in a cyberpunk style.
- Vegas City. This district has over 6,000 parcels. Its focus is gambling, with casinos, nightclubs and shops.
- Dragon City. A district that blends Western and Eastern cultures, with real estate in various architectural styles.
- Fashion Street. A district filled with shops of well-known companies. Visitors can view items using virtual-reality technology and buy them.
Each district holds votes to set internal rules and determine development priorities. Some restrictions apply to construction on private land.
Landowners choose a district’s architectural style and allocate profits. District budgets are distributed via the DAO.
How does Decentraland work?
The platform is a multi-layered architecture comprising three layers: consensus, content and real-time.
The consensus layer tracks rights to virtual property. Decentraland uses Ethereum smart contracts to issue non-fungible tokens, including LAND. This layer stores information about the owners of virtual parcels and objects. Parcel coordinates are stored on-chain, along with a link to the file that contains the parcel’s content.
The content layer is a decentralised storage system that uses software such as BitTorrent. Users host the files needed to render the game world and its objects. The storage holds static elements, textures, audio files and object descriptions, as well as data required for scripts.
The real-time layer enables users to interact with the virtual world and with each other. It loads data from storage in real time and connects avatars.
How does Decentraland’s tokenomics work?
The project uses MANA and LAND. In-game items are represented as NFTs.
MANA is an ERC-20 utility token. The initial supply was 2.8bn tokens. As of January 2022 it had fallen to 2.19bn through burning.
MANA is used to buy land, in-game items and services. It is required for constructing buildings and for governance.
LAND is an ERC-721 non-fungible token that represents a parcel in the metaverse. The NFT’s owner controls the territory at the corresponding coordinates.
If a user holds a group of parcels, they can obtain an Estate token (real estate). The crypto-asset can be created from two or more parcels.
During the metaverse’s formation, MANA was used to buy LAND tokens. Land was sold at auctions in December 2017 and December 2018, with the MANA spent being burned.
Who governs Decentraland?
The platform is governed by a DAO, setting it apart from many alternatives. The founders proposed a collective-governance model at launch, but the project was handed fully to the community only in 2020.
Changes are adopted through votes executed by smart contracts—holders of MANA and LAND can vote and make proposals.
Landowners are entitled to 2,000 votes. MANA holders can also participate in governance, but must first wrap their tokens (wMANA). Each token confers one vote.
How is Decentraland evolving?
The project has been around for more than six years. Users still point to software shortcomings and modest visual fidelity.
In October 2021, the developers added support for Polygon, allowing users to mint and move assets on that network. According to the Decentraland Roadmap, the team plans to improve developer tools and add new features.
Many companies have bought virtual land in the metaverse to advertise and sell products. For instance, it hosts a Sotheby’s art gallery and a Samsung store. Decentraland has hosted weddings and even raves, albeit not especially lively ones. Barbados’s authorities are even preparing to open a virtual embassy.
Рассылки ForkLog: держите руку на пульсе биткоин-индустрии!


