What is a Merkle tree?


Key points
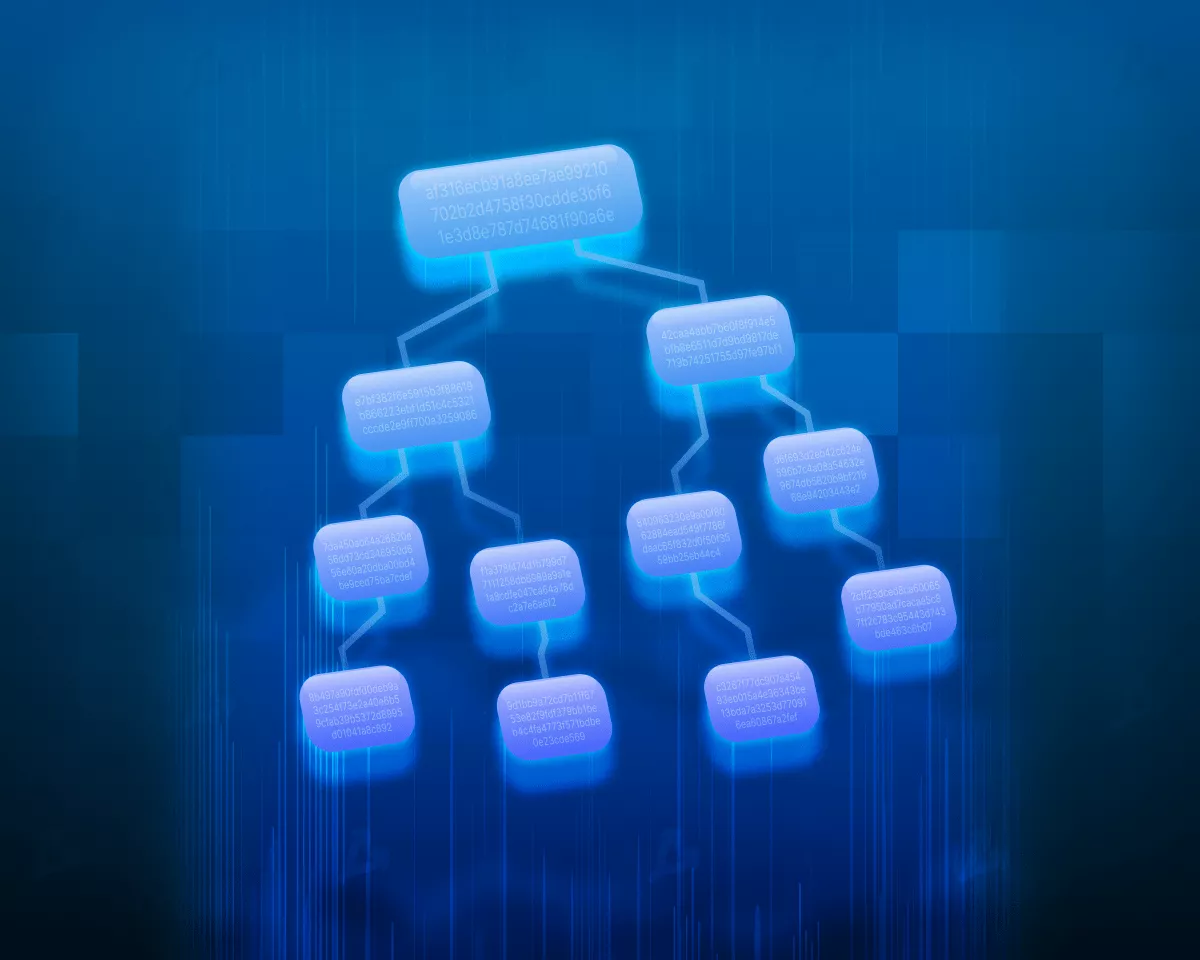
- A Merkle tree (hash tree) is a method that produces a single hash for many fragments of data. It is used to check file integrity and verify information.
- A hash tree can be visualised as a structure whose branches run from the base to intermediate nodes. Leaves at the ends represent fragments of data. At the base sits the root hash (the Merkle root). The latter is a required element of a Bitcoin block header.
- The root hash allows each transaction to be verified. To check one, a client needs only the block header and the transaction’s authentication path. By using a Merkle tree, the amount of computation is reduced, enabling Simplified Payment Verification (SPV).
Who invented the Merkle tree, and when?
The concept of the hash tree was created by Professor Ralph Merkle. He devised a way to represent digital signatures in 1979. The patent for the technology is held by Stanford University.
The scholar proposed using a binary hash tree. Merkle also made significant contributions to cryptography. He is known for his 1987 publication “Digital signature based on a conventional encryption function”.
What is a Merkle tree for?
A centralised system serves data from a single source on which all users rely. The source guarantees the correctness of the information provided.
Blockchain is a distributed database. Information is stored across many independent nodes. A node cannot accept messages from other participants without verification. It must determine whether a block contains valid transactions.
Merkle trees can be used to reduce computational costs. They cut the amount of data that must be downloaded and optimise verification through hashing.
The method is used in the Bitcoin and Ethereum networks and other cryptocurrencies. It produces a data string that verifies a group of transactions. The algorithm is also applied in file systems and databases to detect errors and to synchronise information.
How does a Merkle tree work?
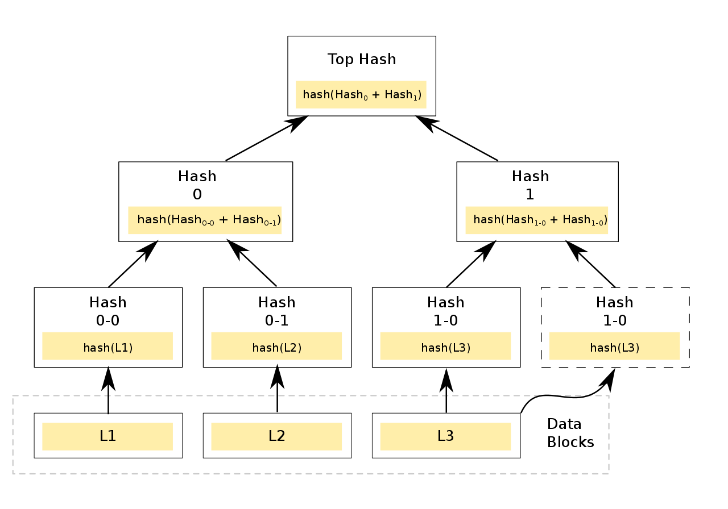
A Merkle tree is built from the bottom up. Values at the leaves are obtained by hashing data fragments. Nodes at the next level contain the hash of the sum of two children. Concatenation is used to combine the data. The operation is repeated for the higher levels until a single hash is obtained. If the number of elements is odd, one is duplicated or carried to the next level unchanged.
Building the tree yields a single hash called the Merkle root. It represents all fragments of data. Thus, a Merkle tree is a one-way hash function.
The algorithm yields a binary structure in which node values are formed from two strings. This allows a large volume of data to be verified without recomputing hashes for every fragment. The computational cost of checking a single element is much lower.
To verify the correctness and integrity of an array, the root hash must be compared with a reference value. Fragments may be transaction data or parts of files.
How is the Merkle tree used in Bitcoin?
Bitcoin’s blockchain is formed from blocks appended to the end of the chain. They contain data on transfers between users. The number of transactions and the amount of information vary, so a block does not have a fixed size.
To optimise computation, Bitcoin nodes form headers. These include:
- the block version number;
- the hash of the previous block;
- the Merkle root;
- a timestamp;
- the mining difficulty target;
- the nonce used to generate the block.
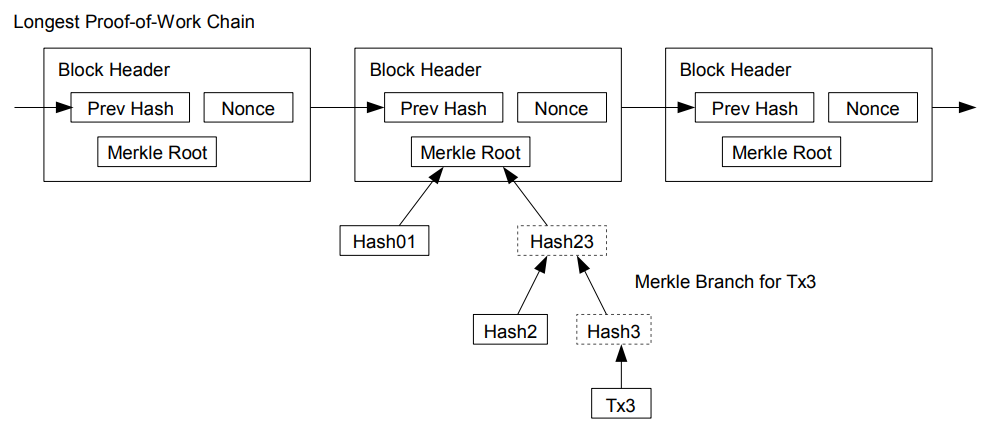
The header does not include transactions and occupies 80 bytes. As it is created every ten minutes, the data volume grows by 4.2 megabytes a year.
Transaction information is hashed to obtain their identifiers. Transfer data are stored in hexadecimal format. The Merkle root represents all transactions in the block. To find it, a Merkle tree is built. The data are processed as follows:
- Compute the hashes (identifiers) of the transactions included in the block: hash(L1), hash(L2), hash(L3), and so on. These form the leaves of the tree.
- Place at the next level hashes of the sum of two neighbouring identifiers: hash(hash(L1) + hash(L2)). In a binary tree the number of nodes at each level must be even. Otherwise, the hash in the last cell is duplicated and placed in an additional element.
- Repeat hashing the sum of data until the Merkle root is obtained.
The resulting hash confirms the validity of each transaction. When forming the blockchain, nodes use only headers of previous blocks.
In August 2017 the Segregated Witness protocol upgrade was implemented. It uses a different structuring of transaction data, which reduces block size. Adoption of the upgrade reduced the load on Bitcoin’s blockchain.
What are the advantages of a Merkle tree?
Hash trees simplify checking that a transaction belongs to a given block and preserve data integrity during transmission. The method is necessary for Simplified Payment Verification. Satoshi Nakamoto proposed using SPV in the Bitcoin white paper.
If a node has ample computing resources, it can download all blocks and compute the hash of every transaction, then form Merkle trees. These allow data integrity and each operation’s validity to be checked. If a node’s resources are limited, it can request only the block header and the transaction identifiers.
Light clients download the header and the authentication path (Merkle proof) for the transaction being verified. They request this information from a full node. The authentication path includes hashes from each pair of tree nodes along the path from the root to the transaction.
To verify a transaction, the Merkle root must be obtained. The transaction is confirmed if the resulting hash matches the string contained in the block header. It is practically impossible to find the required Merkle root from a different data set, which guarantees the operation’s validity.
The SPV method lets a light client interact efficiently with the blockchain and reduces the amount of data to download. For example, a block with five transactions might be 500 kilobytes, while a Merkle proof takes only 140 bytes.
Which hash tree does Ethereum use?
A binary Merkle tree suits an array represented as a list. Its structure is unchanged, which is convenient for hashing transactions. Ethereum uses a different representation — a prefix tree.
The latter stores information in an associative array. Strings serve as keys that determine the positions of elements. To form the structure, the branches of the tree are denoted by different symbols so that an element’s key uniquely identifies it.
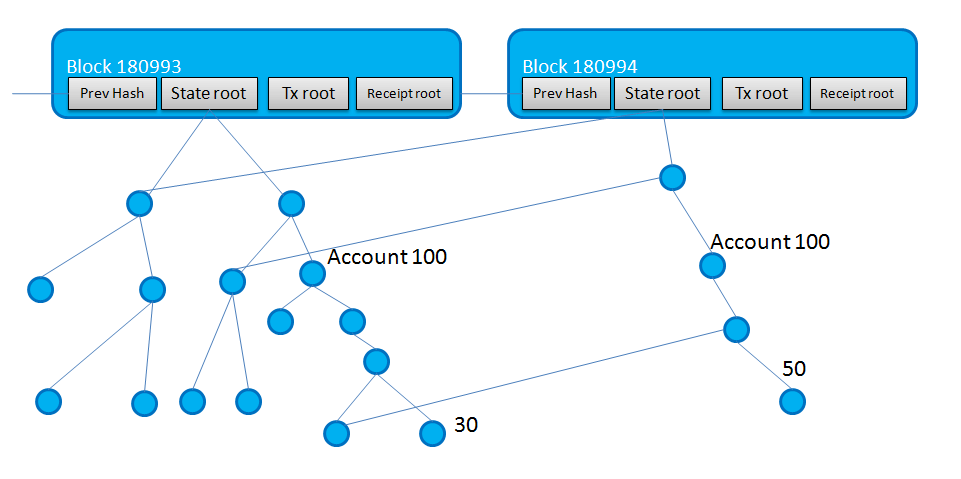
Unlike Bitcoin, Ethereum’s blockchain uses three hash trees:
- transactions;
- state;
- a tree containing data on the results of executing transactions.
The block header includes three root hashes. Ethereum allows the creation of light clients capable of a basic set of operations:
- check whether a transaction is in a block;
- confirm the existence of a specific address;
- determine a user’s balance;
- learn the result of a transaction or a smart contract execution.
These actions are performed without downloading full blocks. Hash trees simplify computation, allowing light clients to run on personal computers, laptops and smartphones.
The algorithm for processing transaction data in Ethereum is similar to that in Bitcoin. Working with the state tree is more complex. The key of an array element is determined by the user’s address, and its value represents the account balance.
A feature of the hash tree is the need for frequent data updates and for adding and removing addresses. Implementing the algorithm requires a mutable structure. Its parameters are constrained to prevent a DDoS attack that would let an attacker create a tree that is too deep. Otherwise, updates and operations would take significant time.
The tree root must be determined solely by the data and must not depend on its parameters. Hence, updates must be possible in any order.
The prefix tree solves these difficulties. In Ethereum, each element of the structure has 16 children. This approach is optimal for encoding nodes in hexadecimal format.
In a prefix tree, to obtain a key you specify in sequence the symbols corresponding to the branches. They define the path from the root to the chosen element. The value at a key is dynamic, allowing new nodes to be added or removed.
Further reading
Рассылки ForkLog: держите руку на пульсе биткоин-индустрии!


