
LayerZero and StarkNet: on the path to interoperability and scalability
Ethereum remains in urgent need of scaling, as evidenced by the rapid rise in gas prices amid market activity. The cost of exchanging ERC-20 tokens or providing liquidity in AMM-pool of a decentralised exchange can sometimes reach several tens, and even hundreds, of dollars.
In response to the situation, developers are diligently working on new layer-2 solutions (L2) and cross‑chain bridges, aiming to make them as efficient and secure as possible. According to L2BEAT, the combined TVL of the segment since the start of the year has grown by more than 150%, crossing the $10 billion mark.
In this article we briefly examine the features of the promising projects — StarkNet and LayerZero.
- StarkWare’s developers are focused on increasing the technology’s efficiency, reducing transaction costs and decentralising the decision-making process. The latter may indicate an upcoming utility-token release.
- The LayerZero protocol aims to improve cross‑chain communication efficiency without compromising security. This is particularly relevant in light of recent cross‑chain bridge hacks.
- Many market participants expect future airdrops from the aforementioned projects and therefore seek to engage in the relevant ecosystems.
StarkNet
StarkNet, from the Israeli company StarkWare, is a decentralised Layer-2 scaling solution for the second-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalisation, based on the ZK-STARK mechanism.
«It provides high throughput, low gas costs and preserves the security levels inherent to the Ethereum mainnet», — said on the project’s site.
The head of the project is the renowned cryptographer Eli Ben‑Sasson, a Technion professor and co‑inventor of the STARK technology. Among other co‑founders: Mikhail Ryabtsov (co‑inventor of ZK-STARK), Uri Kolodny and Alessandro Chiesa (co‑founder of Zcash).
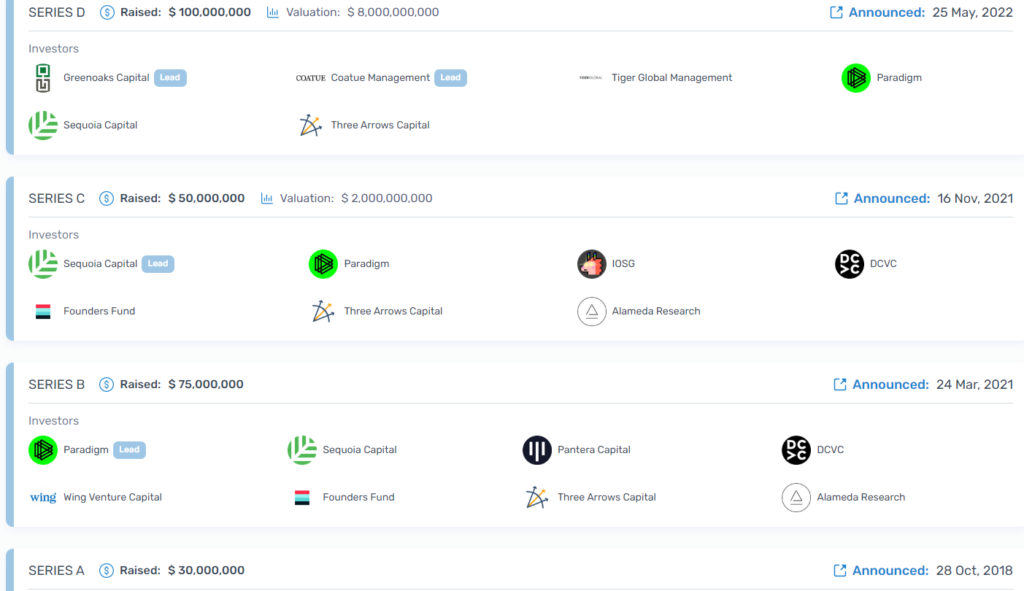
Since its inception in 2017, the firm has raised more than $280m. It has attracted funding from Paradigm, Sequoia Capital, Pantera Capital, Multicoin Capital, Coinbase Ventures, and Ethereum co‑founder Vitalik Buterin.
In May 2022, following a Series D round of $100 million, investors valued StarkWare at $8 billion.
Core products are StarkEx and StarkNet. The former is based on a SaaS model and allows decentralised applications to meet specific needs. It is used by platforms such as dYdX and Sorare.
The second product is a permissionless solution for Ethereum based on Rollups. It enables developers to build and deploy their own smart contracts and to interact with other applications.
It is envisaged that in the future StarkEx will become the project’s “third level,” deployed on top of StarkNet for specific DeFi protocols to simplify and cheaper their usage.
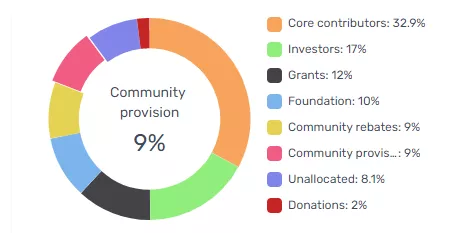
The developers at StarkWare have already released the governance token STRK, an ERC-20 standard, for investors, employees and the development fund. The coin could enter free circulation in 2023.
The asset is intended to contribute to decentralising the network and is meant to perform three main roles:
- participation in governance via staking;
- payment of transaction fees in StarkNet;
- application in the consensus mechanism.
According to the project’s roadmap, in 2023 developers focus on increasing the technology’s efficiency and reducing transaction costs. In 2024 the emphasis will shift to decentralising decision-making, which may indicate an upcoming airdrop.
Key features of the technology
StarkNet is a permissionless ZK‑Rollup in which smart contracts are written in its own programming language Cairo. The latter is Turing‑complete and “specifically designed for STARK proofs.”
The StarkWare team launched an alpha version of the mainnet in November 2021.
The StarkNet-based ecosystem includes more than 120 projects, among them:
- wallets Argent X, Braavos and BitKeep;
- cross‑chain bridges StarkGate and Orbiter Finance;
- DEX (JediSwap,10KSwap);
- digital identity services Starknet.id and Dynamic;
- GameFi-projects;
- NFT services, etc.
Like other L2 solutions based on rollups, StarkWare’s technology bundles hundreds and thousands of transactions into batches and cryptographically attests to their validity.
«All transactions in StarkNet are periodically batched, and STARK proofs verify their validity. This approach significantly reduces the computational power required for verification», — explained by Alchemy researchers.
The architecture of the platform has three basic off‑chain components:
- Sequencer (Sequencer) — a server that receives transactions, verifies and batches them into blocks. It currently exists in a single instance and is controlled by StarkWare. As decentralisation advances, network participants will be able to run their own sequencers;
- Prover — responsible for generating cryptographic proofs confirming the integrity of computations performed by the sequencer. Currently there is a single Prover, which generates proofs not only for StarkNet but also for StarkEx;
- pathfinder — a full node for recording transactions and tracking the system state.
StarkNet also has two on‑chain components:
- Verifier — a smart contract on the Ethereum network that receives newly generated proofs from the prover and verifies them. The result is sent to the core;
- Core — a smart contract that receives changes to StarkNet’s global state each time an L2 block is created and its cryptographic proof is successfully verified by the verifier.
StarkWare says this architecture will help StarkNet reduce gas costs by 100–200 times relative to Ethereum.
The technology differs somewhat from solutions based on Optimistic Rollups, used, for instance, in Arbitrum. In StarkNet, the use of ZK‑STARK allows transmitting a proof of authenticity with the transaction. There is no period during which a transaction can be disputed.
In Optimistic Rollups, to speed up processing all transactions are assumed to be valid until proven otherwise. If a node is malicious and allows incorrect operations, a seven‑day window is provided during which the transaction can be challenged and reversed by verifiers.
The main difference between StarkNet and zkSync is that the latter uses ZK‑SNARK technology.
Some cryptographers believe that ZK‑STARK technology:
- is more secure at all stages of setup and operation;
- potentially up to 10x more scalable than ZK‑SNARK;
- resists attacks using quantum computers.
«StarkNet hopes to make crypto applications accessible to all. And this is the first ZK‑Rollup capable of offering a general‑purpose smart contract platform on a fully composable network», — noted the Alchemy researchers.
In August 2022, StarkWare launched on the Ethereum mainnet the L2 scaling technology using recursive proofs, deployed in applications built on StarkNet and StarkEx.
The developers emphasised that the new solution not only reduces fees and speeds up transactions but also “paves the way for L3 and other benefits.”
Eli Ben‑Sasson believes that Cairo‑written recursive proofs could, in theory, bundle up to 60 million transactions into a single Ethereum block (currently fewer than 1,000).
In October 2022, the Nethermind Ethereum client developers launched a fork of the leading decentralised exchange Uniswap into StarkNet. The Warp plugin allowed transpiling software from the Ethereum main language — Solidity.
«Unlike other ZK‑Rollups such as zkSync, StarkNet is not a “zkEVM”. In other words, smart contracts have to be written in the Cairo language», — noted Argent’s developers.
According to them, after converting code with Warp, applications require some optimisation to run properly on StarkNet.
At the end of 2022 Visa explored StarkNet for automated and programmable payments. The team used the Argent wallet in the proof-of-concept.
In February 2023, StarkWare expanded cooperation with the network of decentralised oracles Chainlink. The company also announced open‑sourcing of Prover.
How to interact with StarkNet?
To start with the ecosystem you will need a Web3 wallet (Web3) — a MetaMask wallet (MetaMask) with some ERC‑20 ETH (ERC-20).
You should also install the Argent X browser wallet, available as a Chrome extension.
Click Create a new wallet, tick two boxes in the disclaimer window that appears, and then click Continue.

After this you need to create a password, re-enter it, click Create Wallet and then Finish.
In the browser’s top-right corner open the wallet, switch from Testnet to Mainnet and click Create Account.
Be sure to go to Settings (the gear icon) and click Show recovery phrase. After entering the wallet password you must copy down the seed phrase and store it securely.
To transfer ETH to the Layer 2 network you can use the official cross‑chain bridge StarkGate. Go to the link and in turn click Connect Ethereum Wallet and Connect StarkNet Wallet in the upper-right corner.
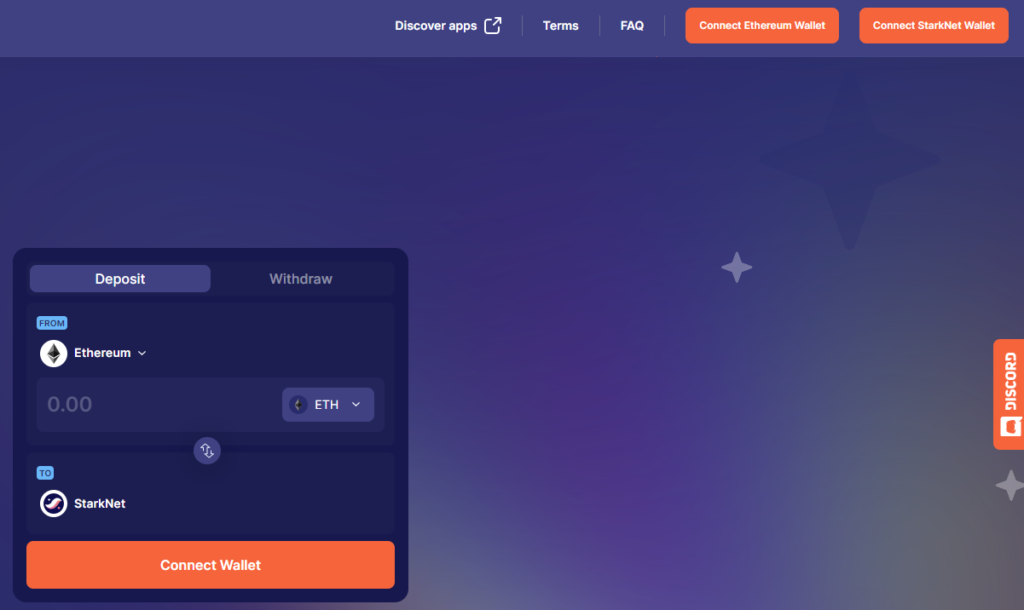
After connecting MetaMask and Argent X you should ensure that Ethereum is selected in the top field and StarkNet in the bottom one.
Then enter the transfer amount, press Transfer and confirm the transaction in MetaMask. It will take a few minutes for the funds to be credited to the L2 network.
The fee may be fairly high as it depends on the current gas price in the Ethereum blockchain. You can monitor it via the Etherscan gas tracker or via the CoinTool browser extension.
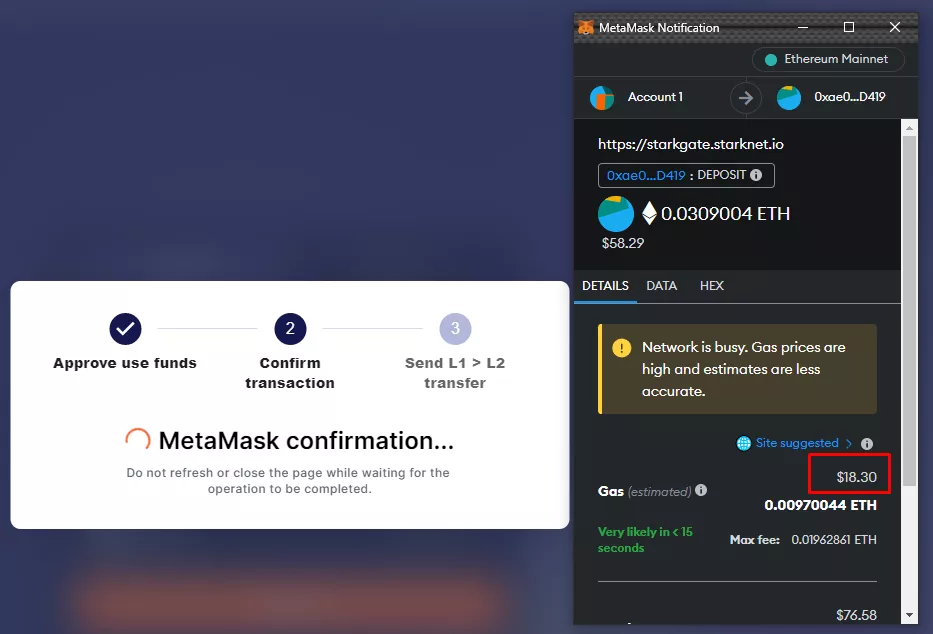
StarkGate also supports transferring ETH from other networks, including Polygon, Arbitrum and Optimism.
Through this cross‑chain bridge you can also withdraw funds back from StarkNet to Ethereum. The fee is significantly lower, but the process takes about a day.
After 24 hours you will need to return to the StarkGate page, reconnect the wallets and in the upper-right corner click Complete Transfer. Then confirm the transaction in MetaMask. A fee will be deducted, depending on the current Ethereum gas price.
There are other unofficial bridges that enable rapid and relatively inexpensive transfers between various networks and StarkNet and back — for example Orbiter and LayerSwap (Cross‑Chain tab).
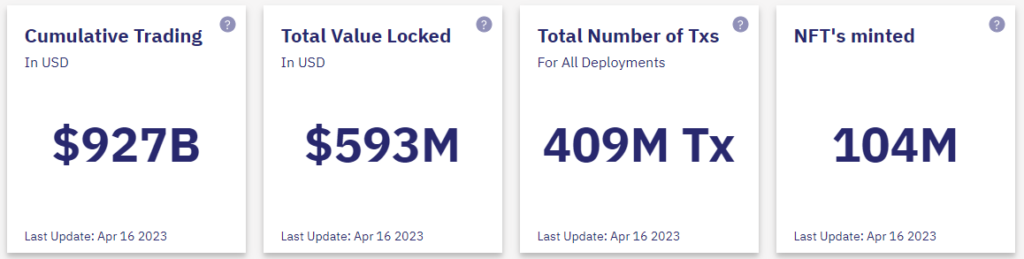
The ecosystem’s total TVL is relatively small — just under $8 million (as of 22.04.2023). Yet the figure is steadily rising.
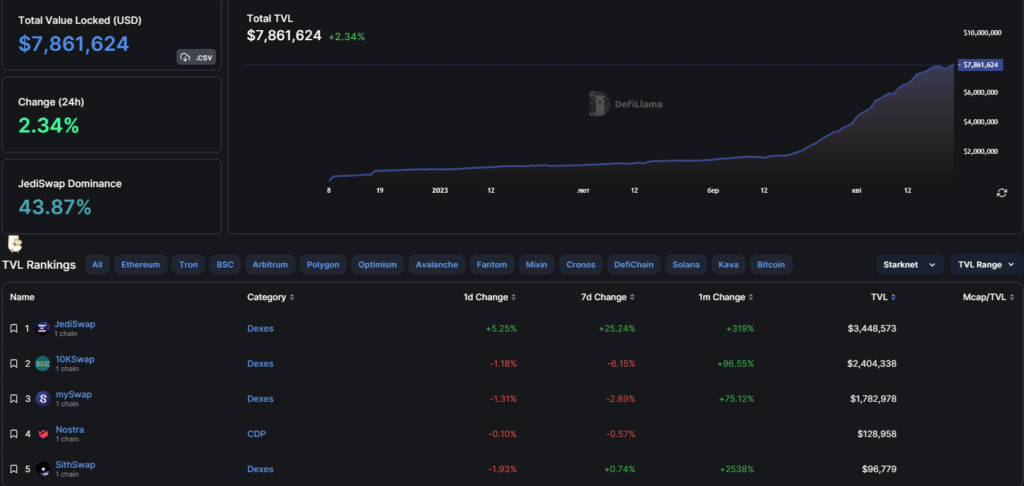
DeFi Llama’s ecosystem ranking for StarkNet features mainly DEXs, the largest of which is JediSwap.
To launch the trading platform’s web interface, click Launch App in the site’s top-right corner. Then in the warning window that appears (this is still an alpha version) click “I understand the risks outlined above” and connect your wallet.
Interacting with this DEX is similar to many other platforms of this kind.
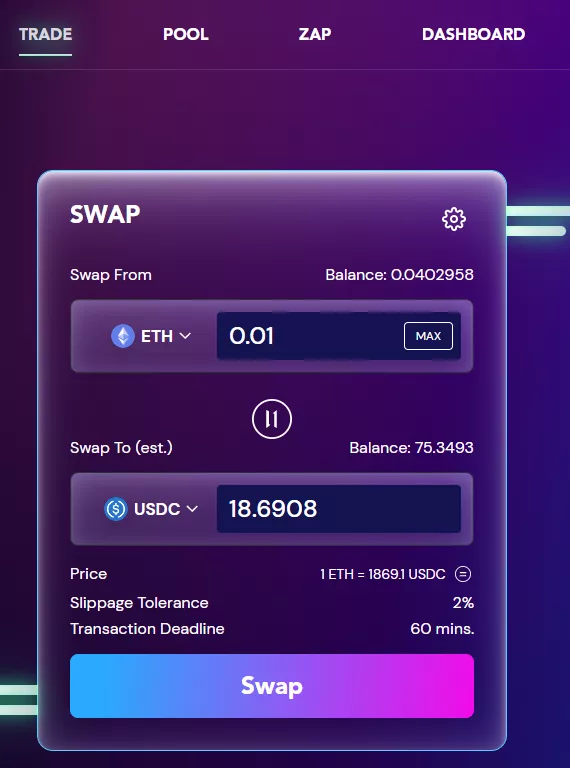
Swap 0.1 ETH for USDC in the Trade tab. When you press Swap and then Confirm Swap, a transaction confirmation window appears in the wallet.
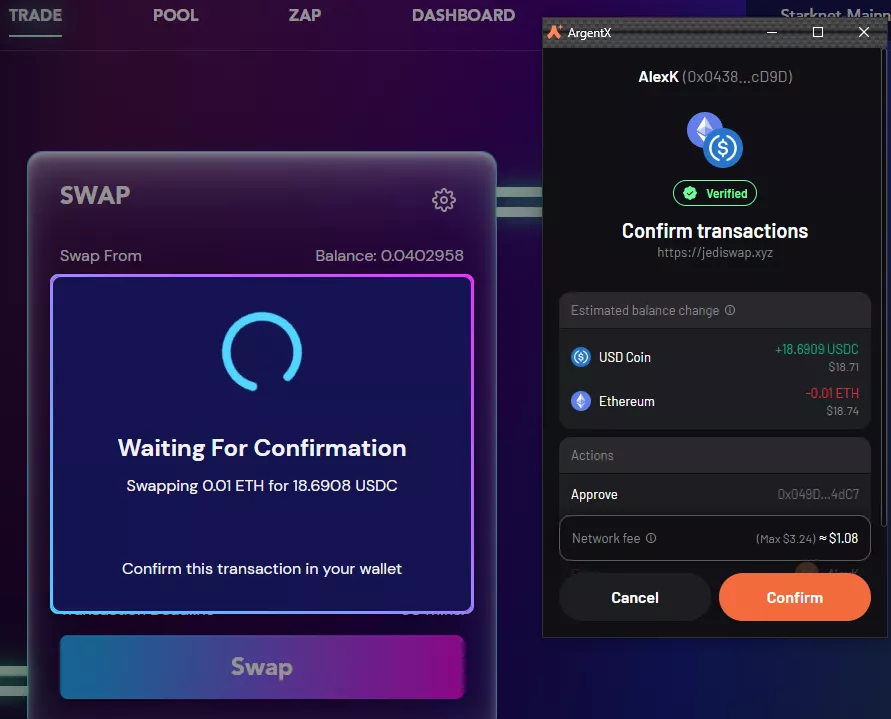
In our case the fee amounted to $1.08.
To place tokens into a liquidity pool, use the Pool tab. This requires clicking Add liquidity and choosing the appropriate assets.
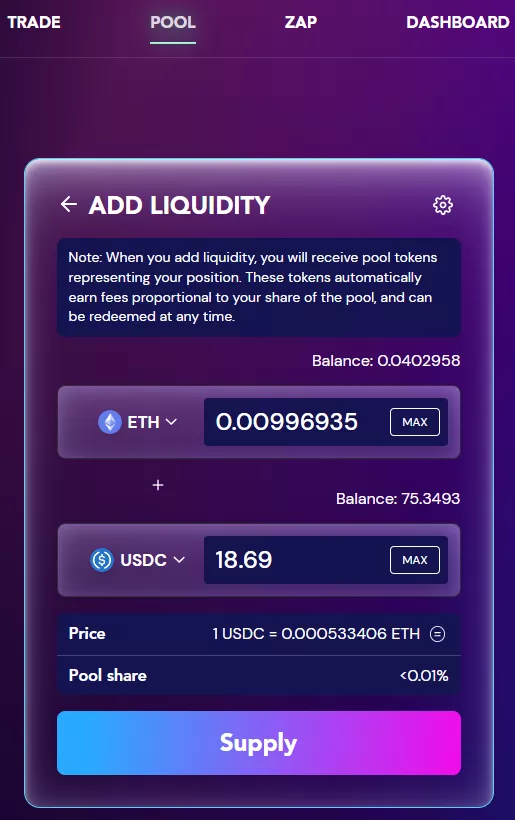
Click Supply, then Confirm Supply and confirm the transaction in the wallet’s pop‑up. In our case the fee was $1.4.
Fees on StarkNet are among the highest of Layer-2 solutions.
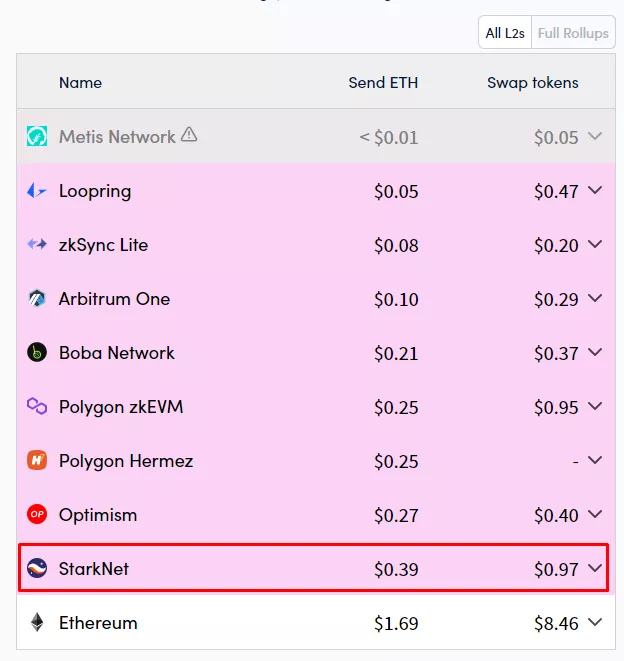
Developers are hard at work on scaling and improving the system’s efficiency. This means that, in the future, fees should fall, boosting competition in the L2 space.
LayerZero
Interoperability remains one of the biggest challenges on the road to development and mass adoption of blockchain solutions. Because of technological differences, many ecosystems operate in isolation, hindering the free exchange of data and assets. LayerZero is designed to remove these barriers without compromising security and decentralisation. According to the developers, the omnichain protocol combines the economic efficiency of Polkadot and the security of Cosmos.
«Because of high fees and changing preferences of DeFi investors, apps spread across multiple blockchains. This has led to significant market fragmentation. LayerZero solves this by linking liquidity across chains», — said LayerZero co‑founder Bryan Pellegrino.
In autumn 2021 the project raised $6m in a Series A funding round led by Binance Labs and Multicoin Capital. Sino Global Capital, Delphi Digital, Spartan and other well‑known venture firms also participated.
In spring 2022 the LayerZero team raised $135m in a Series A+ round at a $1bn valuation. It was led by Sequoia, FTX Ventures and Andreessen Horowitz.
Coinbase Ventures, PayPal Ventures, Tiger Global and Uniswap Labs also participated in funding.
Shortly before the round’s close, the total funds involved in the LayerZero-based cross‑chain Stargate stood at $2.5bn. This was one week after its launch.
Stargate enables token transfers within a single transaction, without locking, minting or burning, and also supports the redemption of wrapped assets.
In spring 2023 the project raised $120m in a Series B round. The cross‑chain protocol was valued at $3bn.
The startup was backed by a16z Crypto, Sequoia Capital, Circle Ventures, Samsung Next, OpenSea, Christie’s and other investors.
Since its inception the project has raised $263m across five rounds.
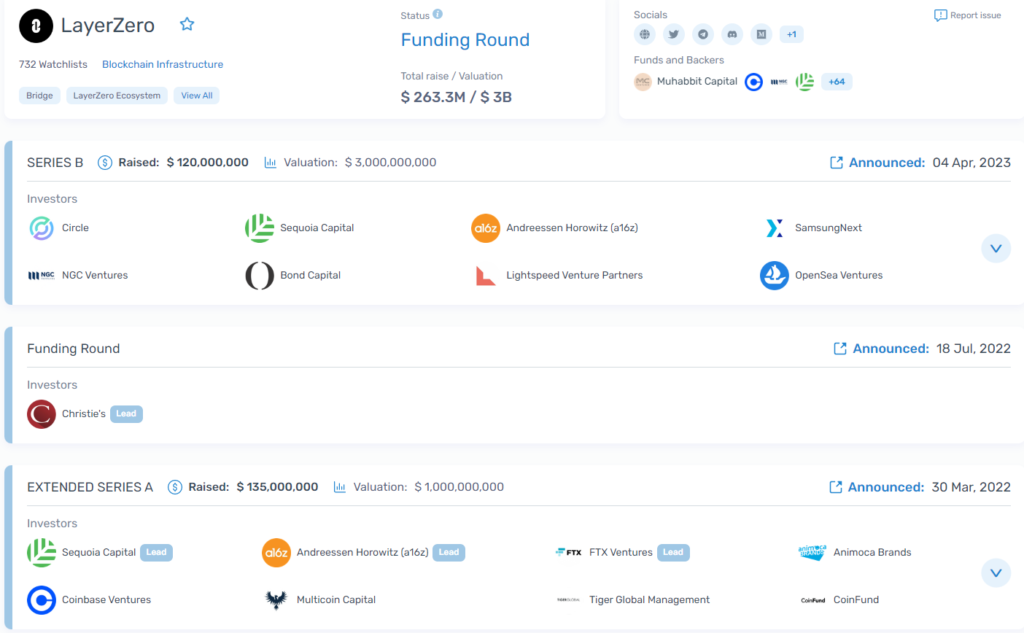
LayerZero supports Ethereum, BNB Chain, Polygon, Avalanche, Fantom, Aptos, Arbitrum, Optimism, and, recently, zkEVM. The protocol has integrated Uniswap, SushiSwap and PancakeSwap.
The solution also enables transferring NFTs via Omnichain Non‑Fungible Tokens.
When working with LayerZero you do not need to rely on a third party. Different chains are connected and interact via decentralised oracles and “Ultra Light Nodes” (Ultra Light Node, ULN). The communication among these forms essentially a single network, where inter‑blockchain interaction is facilitated by the LayerZero Endpoint interface.
This approach is economically efficient and trustless. It enables seamless data exchange — a single liquidity pool can participate in multiple DeFi applications across ecosystems. This is particularly relevant for decentralised exchanges, yield aggregators and lending services that support a wide range of networks.
LayerZero is a modular and extensible system, where adding chains does not require a protocol upgrade. This approach offers greater flexibility and broader scalability. To achieve interoperability there is no need to deploy complex smart contracts and new chains (as, for example, parachains in Polkadot).
Analysts at Nansen recently noted a surge of activity in the Stargate protocol and on the Radiant Capital lending platform built on LayerZero.
3/ @LayerZero_Labs, @StargateFinance, and @RDNTCapital are among the most popular entities on #Arbitrum in terms of users and transactions
7-day users:
LayerZero: 125,715
Radiant: 112,807
Stargate: 111,150Source: https://t.co/7wUny17yxX pic.twitter.com/UKssJS86XP
— Nansen | ?Consensus2023 (@nansen_ai) April 6, 2023
In hopes of a potential ZRO token airdrop, many also use Aptos Bridge and other ecosystem apps on the ecosystem.
2/ Over 3,000 wallets used the LayerZero: #Aptos Bridge in the last 7 days with a $4.2M inflow
The bridge volume/token balances have increased to $20 million, primarily in $USDC, followed by $USDT and $WETH
Source: https://t.co/7ebTGxBTUi pic.twitter.com/FFKyYRgUPq
— Nansen | ?Consensus2023 (@nansen_ai) April 6, 2023
Stargate cross‑chain bridge is similar to other such solutions. As of writing, it supports Ethereum, BNB Chain, Avalanche, Polygon, Arbitrum, Optimism, Fantom and Metis.
You can transfer assets from one network to another in the Transfer section.
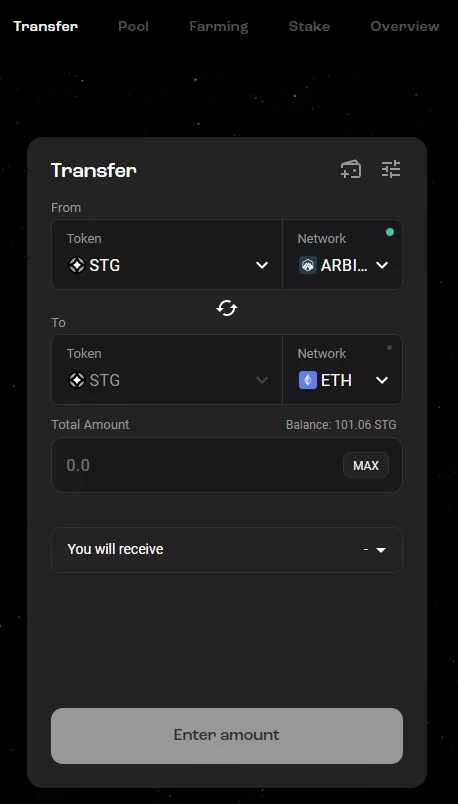
In the Farm tab there is a possibility to earn passive income from stablecoins such as USDT, USDC, DAI and FRAX.
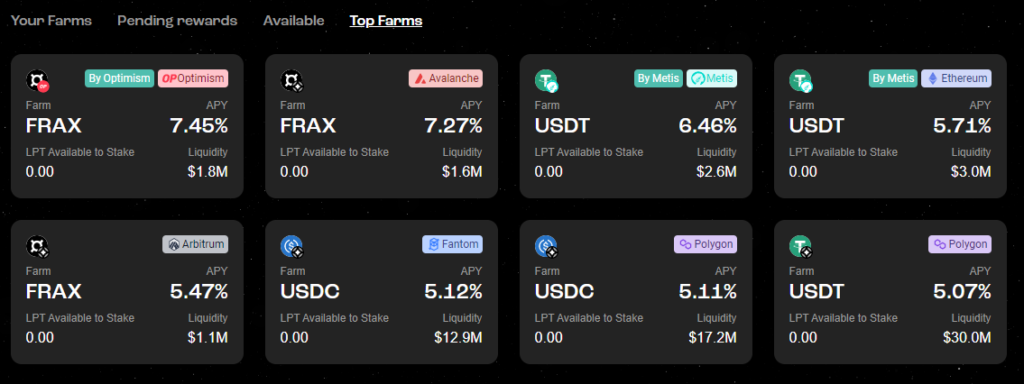
In the Stake section you can stake the utility token STG on the BNB Chain and Arbitrum networks.
Aptos Bridge enables almost instant transfers of assets from various chains to the Aptos network. To interact with the platform you should connect the MetaMask and Martian wallets.
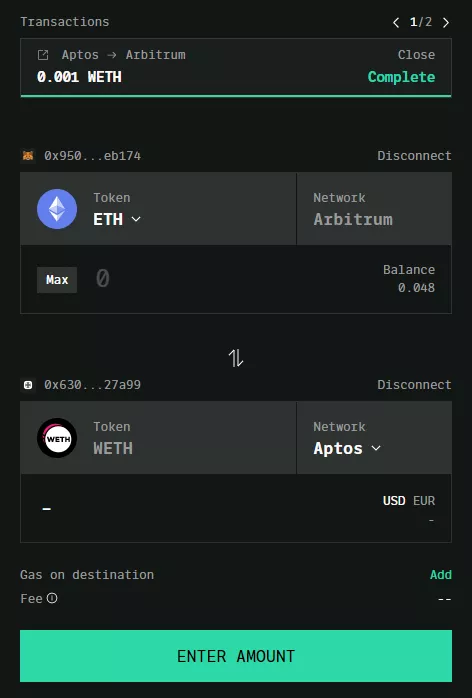
Also on LayerZero are cross‑chain bridges from platforms WooFi, BitcoinBridge and LiquidSwap.
Conclusions
Given the scale of investments, integrations, the roadmap and TVL dynamics, StarkNet has strong prospects to become a major ecosystem with many interesting DeFi applications. A decentralisation trajectory with a subsequent utility-token launch could also be positive for the project.
For now, StarkNet lags behind competitors on cost of fees, which may restrain user activity. However, based on developers’ statements, the technology’s potential remains to be unlocked — and the issue is likely to be resolved.
Interoperability, efficiency and security of inter‑blockchain interaction are a pressing and important area of crypto development. The success of LayerZero will have a significant impact on a broad range of DeFi platforms, including DEXs, lending services and yield aggregators.
Рассылки ForkLog: держите руку на пульсе биткоин-индустрии!


