
How the Alchemix Lending Protocol Became a Driver of DeFi 2.0 Growth
Alongside DEX, lending services are one of the cornerstones of the DeFi segment. With relatively simple interfaces, they allow holders to earn interest and, in a few clicks, borrow funds collateralised by digital assets.
For a long time, the segment has been dominated by projects such as MakerDAO, Aave and Compound. Their TVL stands at $15.15 billion, $13.59 billion and $6.64 billion respectively (as of 10.04.2022). Also gaining traction is Anchor protocol from the Terra ecosystem. Its TVL has already surpassed $15 billion. Gradually lending projects of the DeFi 2.0 concept such as Alchemix, where debt obligations self-amortise and are not subject to liquidations.
- Alchemix is oriented toward higher capital efficiency and minimisation of liquidations through the issuance of synthetic versions of collateral assets.
- The key innovation of the platform is self-amortising loans realised through integration with yEarn Finance.
- Alchemix provides partial liquidation of positions and debt repayment using various stablecoins.
Key features of classic lending protocols
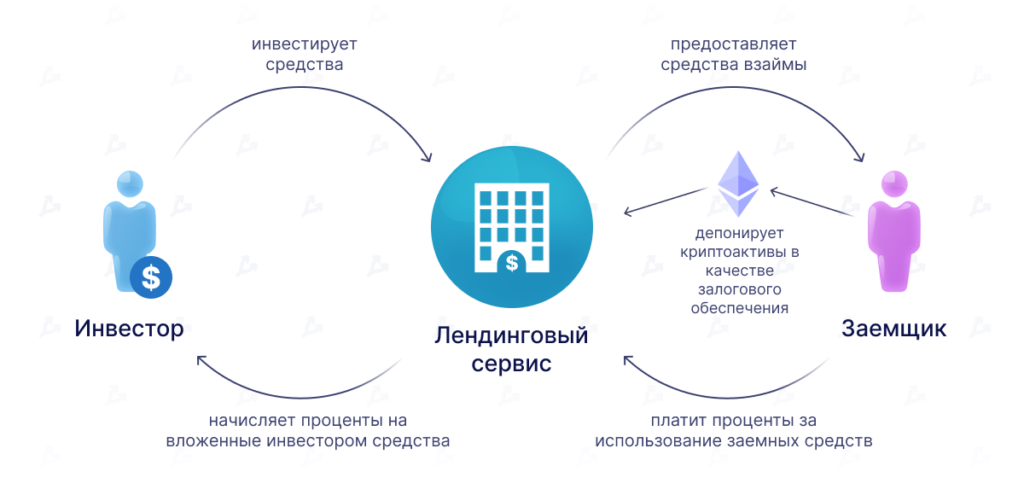
Any lending protocol has supply pools of digital assets and borrowing pools. Each contains a defined set of coins.
Users deposit assets into the supply pool, which gives them the ability to earn interest on their invested funds and borrow coins. The amount of available credit, in a given proportion, is below the value of the assets in the supply pool.
For example, the Loan-to-Value (LTV) parameter for “Wrapped Bitcoin” WBTC on the Aave platform on the Ethereum network stands at 70%. This means that if the collateral is worth $10,000, a user can borrow WBTC worth no more than $7,000.
The surplus collateral lies at the heart of the main difference between permissionless protocols and traditional-finance products, based on partial-reserve banking and KYC.
Another key aspect of lending protocols is liquidations. If the value of the collateral falls below a certain threshold, the user’s collateral assets are forcibly sold.
Alchemix value proposition
Alchemix is a relatively new lending protocol with some distinctive features.
“Alchemix’s self-amortising loans allow the use of a range of tokens without liquidation risk”, as stated on the project’s website.
Loans in synthetic versions of collateral assets allow liquidation risk to be avoided. For example, a user deposits collateral in ETH or DAI and issues the tied assets — alETH and alUSD respectively.
If prices fall, both the value of the collateral and the borrowed funds fall. However, this does not negatively affect debt positions and does not affect the LTV parameter.
This is the key difference between Alchemix and classic lending protocols, where volatile assets such as ETH are typically deposited and loans are taken in stablecoins (as the value of collateral in ETH falls, the loan amount in stablecoins remains unchanged, making the debt position risky).
The platform interacts with the yEarn Finance protocol, created by Andre Cronje. Through this integration, users earn yield on the collateral they deposit.
For example, a user deposits DAI into Alchemix. Yield begins to accrue to the stablecoins immediately thanks to one of yEarn Finance’s strategies. Against the collateral, the user can borrow alUSD — the protocol’s native stablecoin.
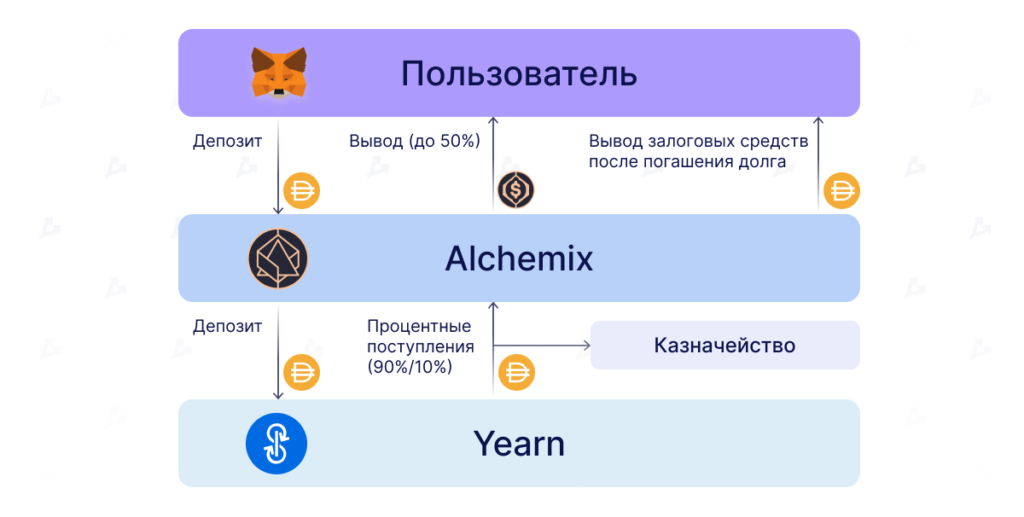
The yield generated by yEarn vault gradually amortises the user’s loan. This approach is more efficient, as it allows for more borrowed funds and minimises liquidation risk.
The protocol’s Loan Ratio stands at 50%. That means a user’s loan cannot exceed half the value of the collateral. In other words, the collateral value must be at least twice the loan amount.
Users can liquidate the collateral, or part of it, at any time to immediately repay the debt expressed in alUSD. Partial liquidation can be useful if users urgently need collateral assets but cannot fully repay the borrowed funds.
Repayment can be made with either the synthetic stablecoin or the more familiar DAI, USDC or USDT.
As of writing, the yield on the Vault on yEarn for the DAI stablecoin stands at just 2.53%. The strategy involves interacting with Compound and Curve to farm the COMP and CRV tokens. The generated tokens are sold for DAI, which is then redeposited into the Vault.
10% of the generated revenue goes to the Alchemix DAO treasury. These funds are used to pay developers, fund various community initiatives, for periodic audits, etc. The remaining 90% goes toward repaying debt positions of users.
To maintain the alUSD peg, an arbitrage system similar to Terra is used.
Suppose that 1 alUSD is cheaper than 1 DAI. An arbitrageur can buy synthetic stablecoins from Alchemix at a discount on one of the exchanges, and then exchange them for an equivalent amount of DAI profitably to repay the debt in their vault.
If 1 alUSD costs more than 1 DAI, the asset can be issued at a discount to market price and then sold.
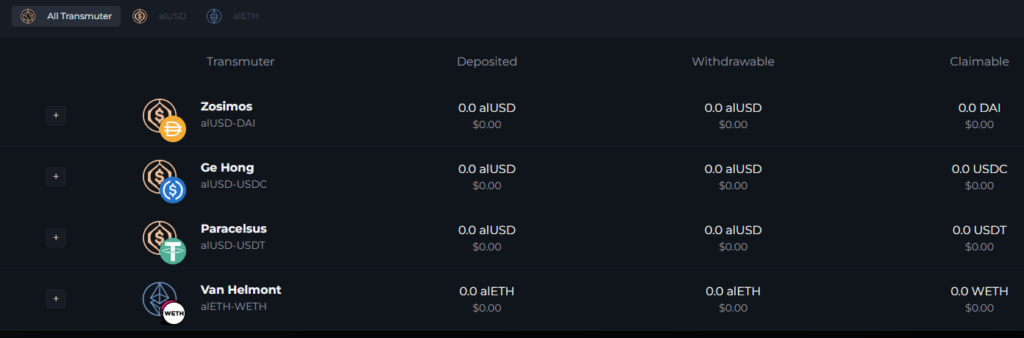
The platform includes Transmuter. It enables 1:1 conversion between WETH and stablecoins and synthetic assets. For example, one can swap borrowed alUSD for DAI, and then use the latter in third‑party DeFi protocols to maximise capital returns.
Alchemix has a native token, ALCX. It is used in governance votes on protocol matters. The token can also be staked or provided in the WETH/ALCX liquidity pool on SushiSwap.
As shown below, in March 2021, soon after the project’s launch, the ALCX price briefly surpassed the $2,000 mark. The asset’s price subsequently went into a free fall.
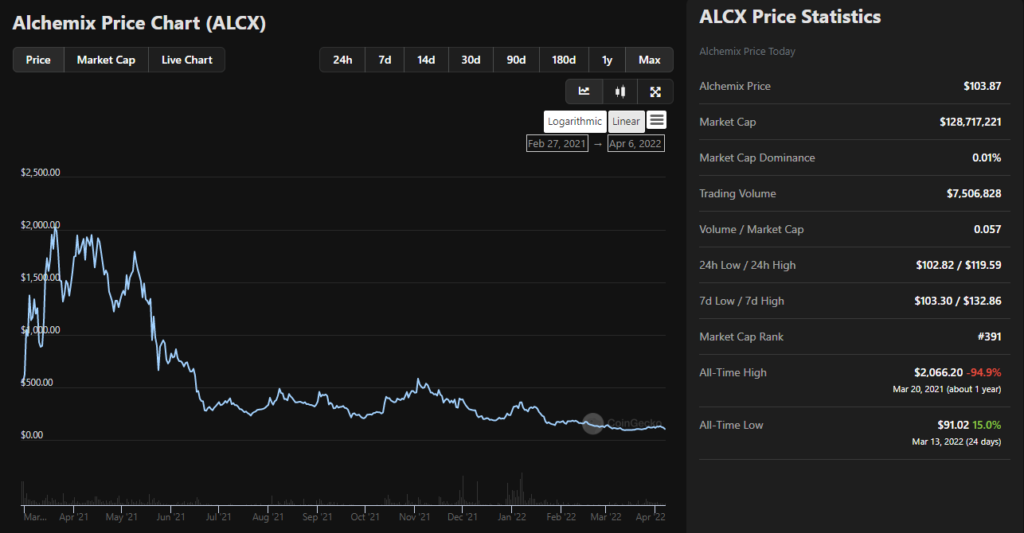
As of writing (10.04.2022), the asset trades near a historical low — just above the $90 mark.
ALCX, ETH and synthetic versions of these assets can also be farmed with the farming feature.
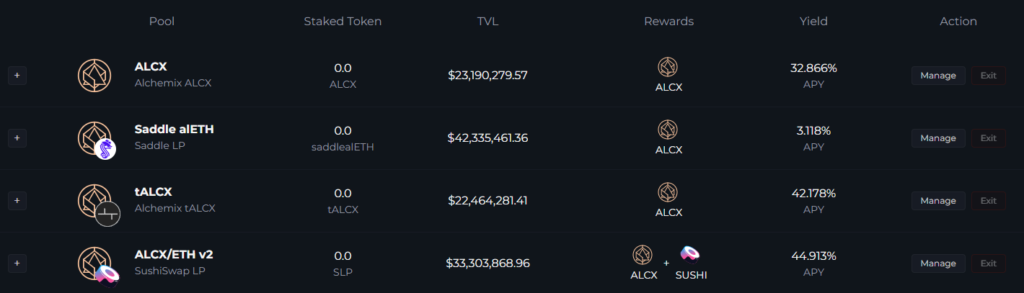
Annual yields of pools (APY) vary significantly. For example, APY for Saddle alETH as of 6.02.2022 is 3.12%, and for ALCX/ETH v2 — 44.91%.
Alchemix 2.0 and the project’s prospects
The first version of Alchemix launched in February 2021. Initially the platform had only two Vaults — for DAI/alUSD and ETH/alETH.
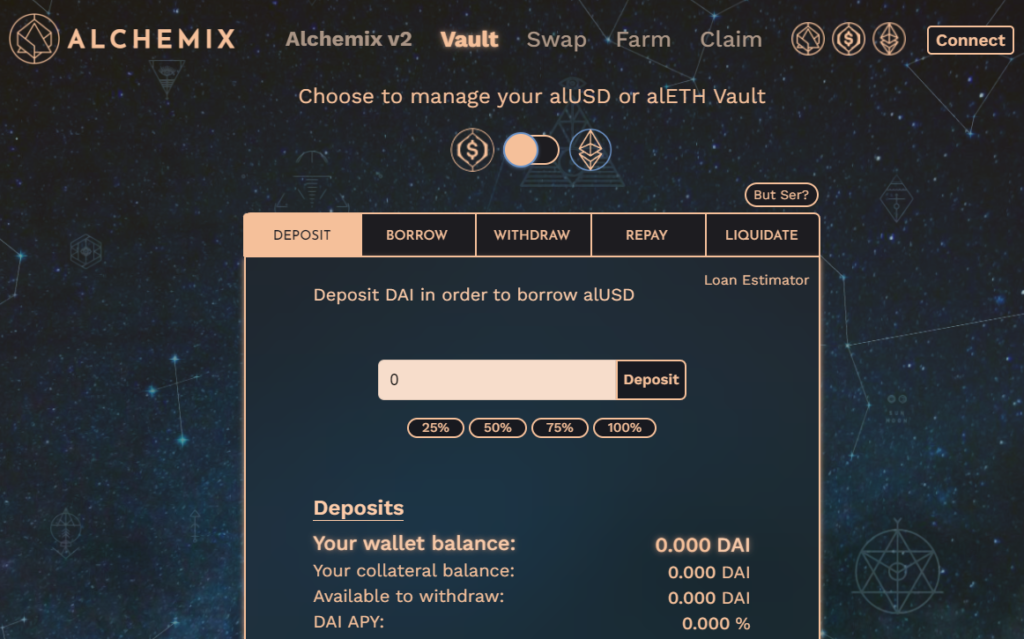
With the launch of version 2 in March 2022, Alchemix’s interface was transformed, and the platform’s capabilities were significantly expanded.
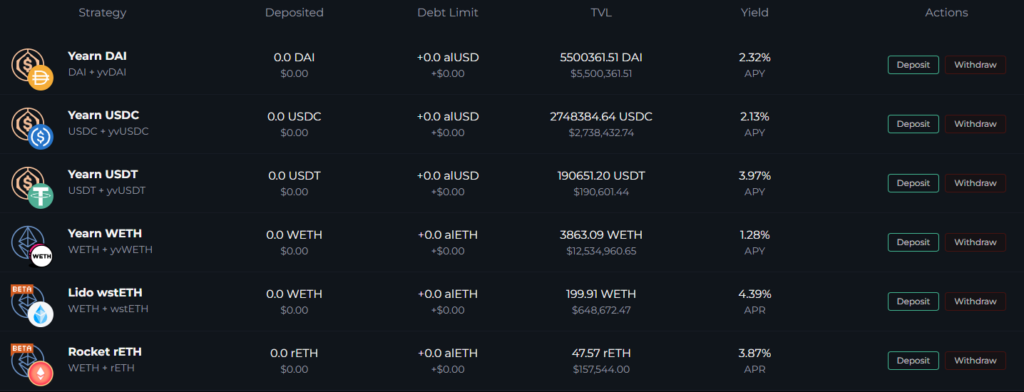
Vaults were introduced on the basis of popular centralized stablecoins USDC and USDT, as well as on wrapped Ether from Lido (wstETH) and the rETH token from the Rocket Pool protocol.
According to the new assets, Transmuter capabilities expanded, the Farms section changed. Scoopy Trooples, the co-founder of Alchemix, announced integration with Aave, Compound and other DeFi protocols in addition to yEarn.
We are initially launching with @iearnfinance as our yield provider, but will soon have strategies that can hook into yield sources from @AaveAave and @compoundfinance and other protocols that share their token standards.
— scoopy trooples (@scupytrooples) March 15, 2022
According to him, new yield strategies and collateral types will appear soon.
More strategies and collateral types will be added over time to Alchemix v2. It is our goal to have our yield sources capture the best yields in DeFi for our users.
— scoopy trooples (@scupytrooples) March 15, 2022
Scoopy Trooples also described the second version as safer than the first.
Conclusions
Alchemix offers an interesting value proposition — developers have radically redesigned non-custodian lending approaches.
By integrating with the yield aggregator yEarn and using synthetic assets, users’ collateral is used efficiently. Debt positions are largely immune to liquidations and are serviced automatically by future interest income.
Among the drawbacks is the relatively low yield of yEarn strategies at the time of writing. There is also no support yet for newer-generation networks such as Fantom and Avalanche with their fast and inexpensive transactions. However, given optimistic statements by developers and rising popularity of cross-chain solutions, these issues are likely to be resolved soon.
In the future, one can expect no less original approaches within the DeFi 2.0 concept and new solutions that incentivise active participation in decentralized ecosystems.
Subscribe to ForkLog’s channel on YouTube!
Рассылки ForkLog: держите руку на пульсе биткоин-индустрии!


