Margin trading vs futures: what is the difference and which to choose?

Key points
- Margin trading involves spot-market transactions using borrowed funds. Traders pay a fixed hourly rate for using them.
- Futures trading involves contracts that track changes in an asset’s price. Users trade them against posted collateral and pay or receive a funding rate on open positions every eight hours.
- The main distinction is maximum leverage — up to 125x for futures versus up to 10x for margin.
What is leverage?
Leverage is a mechanism that lets a trader open a position larger than the cash on their account. It can amplify potential gains on long positions and allow profits from falling prices via short sales.
The leverage ratio is the size of the position, including borrowed assets, relative to the trader’s own funds. For example, with 10x leverage a user with a $1,000 deposit can buy or sell $10,000 worth of assets.
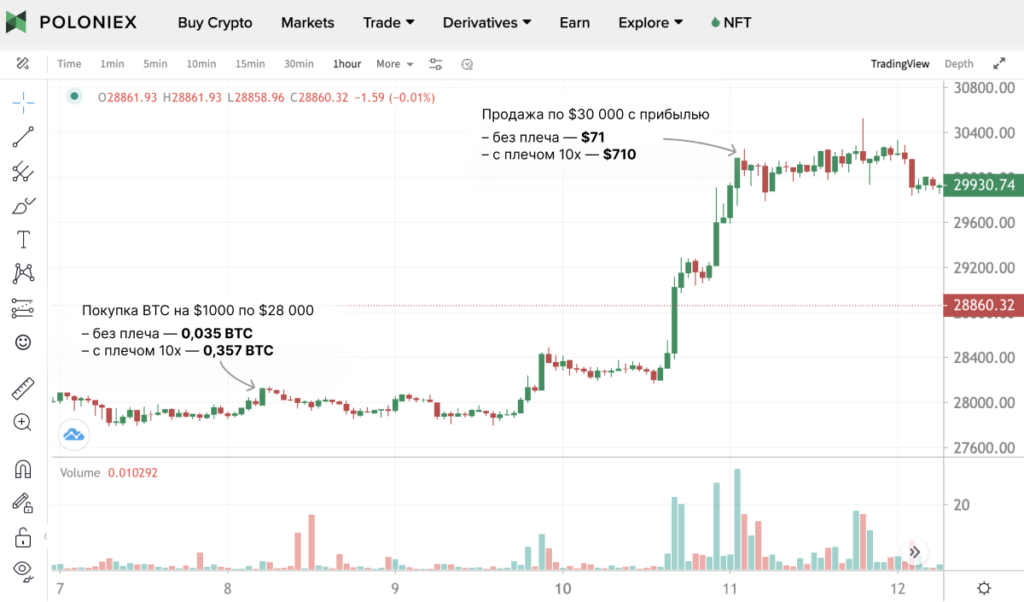
Leverage magnifies losses as well as gains. With 10x leverage on a long, a 10% drop in the asset’s price can wipe out the entire margin.
What is margin trading?
Margin trading is leveraged trading on the spot market. A trader buys and sells cryptocurrencies that can then be withdrawn to external wallets.
To open a position, the trader borrows additional funds against collateral — the margin. The lender is the trading platform or depositors in its investment products.
What is futures trading?
Futures trading involves derivative contracts (futures), where the parties agree to buy or sell an asset in the future at the price fixed when the trade is executed.
To open a position on the futures market, traders must post collateral sufficient to cover potential losses.
Crypto exchanges list perpetual, cash-settled futures: buyers and sellers bet on price moves and settle in stablecoins. They cannot withdraw contracts or request delivery of cryptocurrencies.
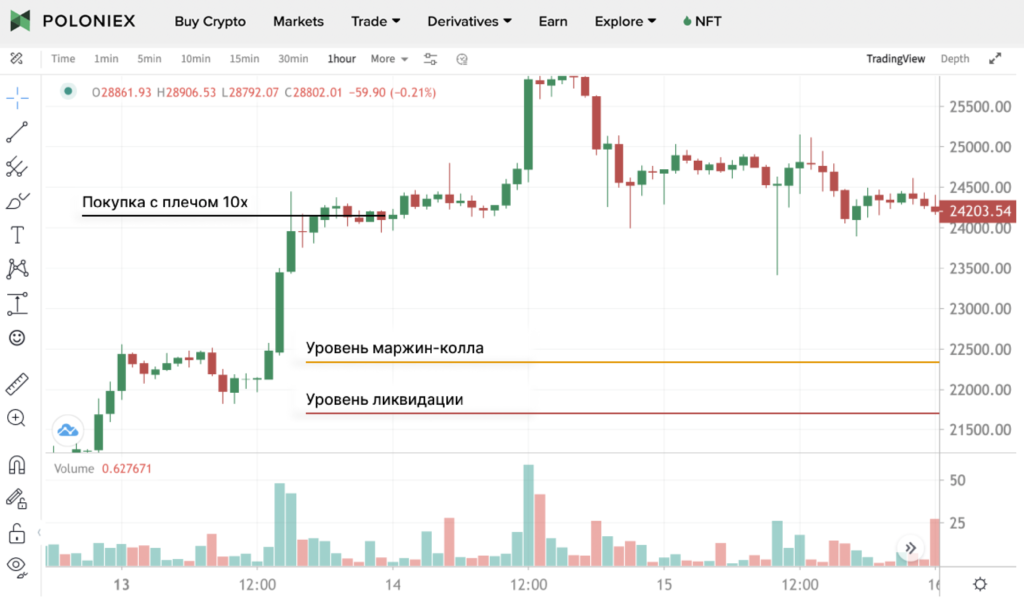
What are margin calls and liquidations in leveraged trading?
A margin call is an exchange notice asking a trader to add margin to a losing position. For example, Poloniex sends a margin call when the loss reaches 75% of the margin.
Liquidation is the forced closure of a position to return borrowed funds to lenders. Crypto exchanges liquidate when the loss reaches 100% of the collateral.
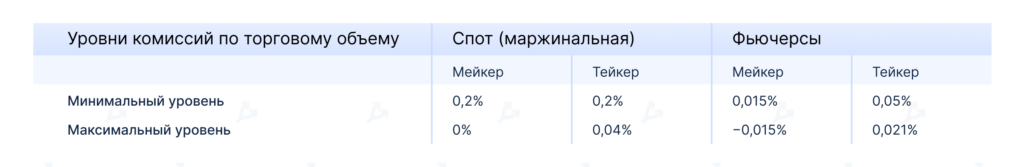
What fees apply on margin and futures markets?
Trading fees are always lower on the futures market. Spot trading requires the exchange to move coins between the buyer’s and seller’s accounts; futures do not.
When holding positions on both markets, traders also pay:
- on margin — an hourly interest rate for borrowing. The average rate for bitcoin, Ethereum and Tether ranges from 3.65% to 1.27% per annum, depending on trading volumes;
- on futures — a funding rate every eight hours. If a contract trades below spot, buyers pay sellers, and vice versa. For instance, the cumulative funding for holders of long positions in BTCUSDTPERP on Poloniex in April was 0.754%, or 9.05% annualised.
How do margin and futures trading differ?
- Margin trading takes place on the spot market, while futures trade on the crypto-derivatives market. In the former, buyers can withdraw assets to external wallets; in the latter, they cannot.
- The maximum leverage on the margin market is up to 3x; on the futures market, up to 100x.
- The position-size limit is up to 120 BTC for margin and up to 25 BTC for futures.
- There are more futures contracts than pairs available for margin. For example, Poloniex lists 38 futures, while only 12 cryptocurrencies are available for margin trading.
- Thanks to higher leverage, the futures market is more volatile. This increases the risk of liquidation and stop-order closures.
- Margin trading typically requires two cryptocurrencies for longs and shorts. On the futures market, the trader posts collateral in a single currency regardless of direction.
Which suits beginners — margin trading or futures?
Margin trading is better suited to beginners. It entails lower financial risks thanks to:
- lower leverage up to 3x;
- lower spot-market volatility;
- a fixed hourly borrowing rate;
- trading limited to the most popular and liquid cryptocurrencies.
Futures trading can yield higher returns but comes with greater risks:
- liquidations when using leverage up to 100x;
- accidental stop-loss triggers when trading low-liquidity contracts;
- slippage when using market orders during periods of high volatility.
It suits traders who already manage capital well and can profit from market volatility and high leverage.
Рассылки ForkLog: держите руку на пульсе биткоин-индустрии!


