
Cows in the Dark Forest: A Review of the CowSwap Decentralized Exchange
In May, trading volume on Ethereum-based decentralized exchanges (DEX) surpassed the $115 billion mark. Almost 60% of this volume was on Uniswap.
The growth of the DeFi sector has been accompanied by hacker attacks and fraudulent schemes. But a relatively new risk for users of decentralized exchanges has become Miner Extractable Value (MEV).
In late April, the project Gnosis unveiled a protocol for decentralized exchanges with MEV protection and a Coincidence of Wants (CoWs) order-matching mechanism. We discuss Gnosis Protocol v2 (GPv2) and test the DEX CowSwap.
What MEV Is
In 2019, cryptocurrency and smart-contracts researcher Phil Daian published the paper “Flash Boys 2.0: Front-running, Transaction Reordering, and Instability of Consensus on Decentralized Exchanges.” In it, Daian introduced Miner Extractable Value (MEV).
MEV is the profit that miners can earn by selectively including or reordering transactions within blocks.
Imagine: on Uniswap there is an arbitrage opportunity with potential profit of $10,000. A trading bot spots it and submits an Ethereum mempool transaction. There are two scenarios that may follow:
- the miner refuses to include the transaction in the block and undertakes the arbitrage trade themselves. In that case, they would receive $10,000. This is MEV;
- other bots notice the transaction and offer the miner a higher fee. A race for the right to execute the arbitrage (Priority Gas Auction, PGA) ensues. The winner earns the arbitrage profit after deducting the fee. For example, $9,000 if the fee is $1,000.
More about MEV can be read in Charles Noyes’s “MEV and I”, as well as Dan Robinson and Georgios Konstantopoulos’s “Ethereum Is a Dark Forest” and “Escape from the Dark Forest”.
What CowSwap Is and the Gnosis Protocol
CowSwap — a decentralized exchange with DEX-aggregator features based on Gnosis Protocol v2 (GPv2).
The Gnosis team released the first version of the protocol in early 2020. Over the next six months, developers studied the protocol’s weaknesses. They found that gas costs prevented market makers from offering tight spreads. Fragmented liquidity also affected asset prices. In April 2021 the project introduced the second version of the protocol, which addresses this problem.
By mid-year, Gnosis and the developers of the AMM protocol Balancer planned to deploy Balancer-Gnosis-Protocol (BGP) on Ethereum. It would combine Balancer V2’s gas-cost-reduction algorithm with the price-determination mechanism of Gnosis Protocol V2 with MEV protection. This integration would offer CowSwap users better prices.
As of publication, CowSwap was in alpha testing.
How GPv2 Works and How It Protects Against MEV
Gnosis Protocol v2 employs technologies such as:
- Coincidence of Wants (CoWs). When one trader wants to buy an asset and another wants to sell the same asset, there is a “coincidence of wants.” The protocol executes such orders directly, without an external market maker or liquidity provider.
- Batch Auctions (BA). The protocol groups orders into batches (BA). Inside a batch, token prices are homogeneous and do not depend on the order of orders. This helps protect traders from Miner Extractable Value.
- Gas Free Transactions (GFT). A user confirms an order off‑chain, without paying gas. CowSwap, meanwhile, optimises the cost of execution: applying CoWs, monitoring prices on other DEXs and considering the gas price to include the transaction in a block. Users pay a fee if the protocol executes the transaction on their terms.
CowSwap submits users’ orders to GPv2. The protocol bundles orders into batches (BA) and passes them to the solving participants (solvers). The solvers search for the most advantageous market price and are rewarded in Gnosis tokens (GNO).
Any user can become a solver. To do so, one must:
- lock 100 GNO in GnosisDAO;
- obtain the approval of participants in the decentralized autonomous organization;
- install the software to create a BA.
When the best prices are found, the protocol executes the orders in the batch. First it looks for CoWs trades: when there is a match of wants, the smaller order is executed against the larger one. It then searches for liquidity on other DEXs to complete the remaining orders.
After the Balancer-Gnosis Protocol integration, Balancer will become one of CowSwap’s main liquidity sources.
Testing the Exchange: Exploring the Interface and Executing a Swap
We tested CowSwap by swapping Wrapped Ether (WETH) for the Gnosis token (GNO). To do so, we visited CowSwap.exchange and connected an Ethereum wallet.
We selected tokens for swapping. By default CowSwap shows Gemini’s tokens. You can connect tokens from other exchanges — click the Manage button. You can also input a token address manually.
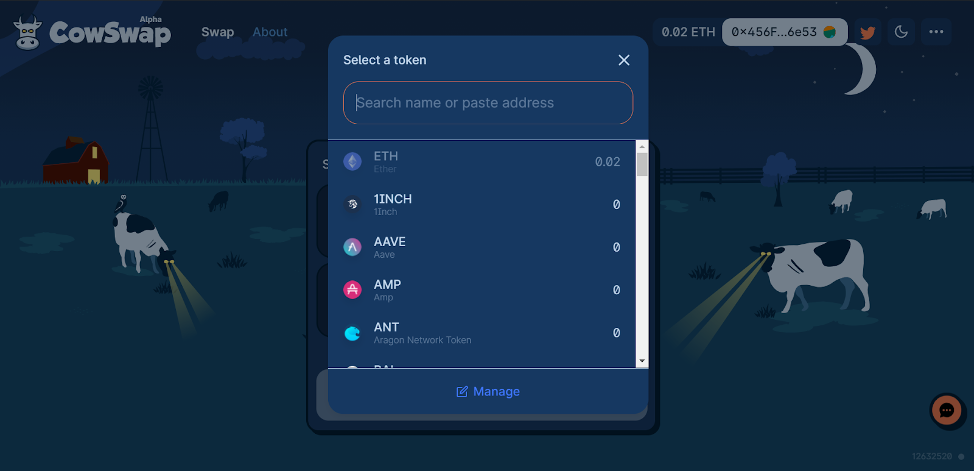
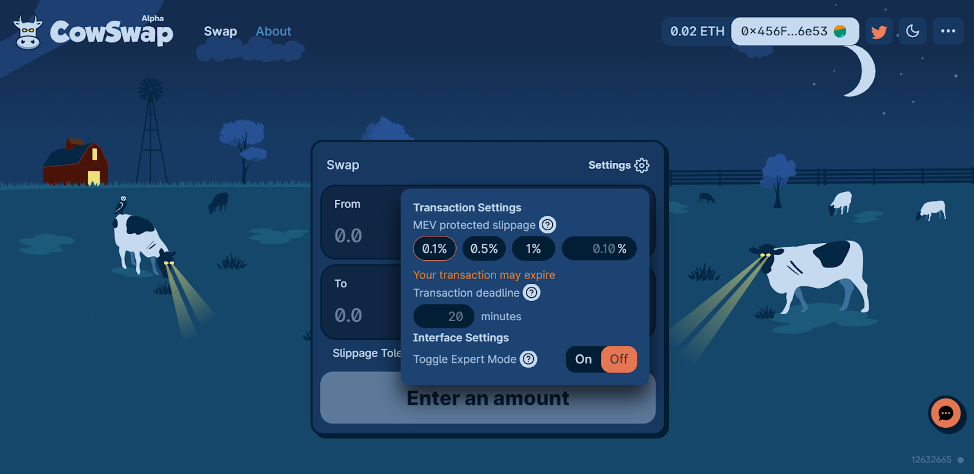
We specified the amount of tokens and configured the transaction. Selected:
- Price slippage tolerance. CowSwap will execute the order within a tight spread — 0.1–1% of the quoted price.
- Deadline. The exchange will cancel the order if it cannot execute the transaction within the specified period.
CowSwap offers an Expert mode. In this mode the exchange does not require confirmation before submitting transactions and allows trades with high slippage.
When attempting to sell 0.1 ETH, the exchange offered to wrap the cryptocurrency into an ERC20 token called WETH. We bought the token and paid a transaction fee of 0.0011591 ETH.
We then checked the transaction settings and authorised CowSwap to spend tokens from the wallet. We clicked Approve WETH and confirmed the operation in MetaMask.
We moved on to the swap itself: clicked Swap and confirmed the transaction in MetaMask.
CowSwap charges a swap fee equal to the value of the trade. In our case it amounted to 0.0540555 GNO.
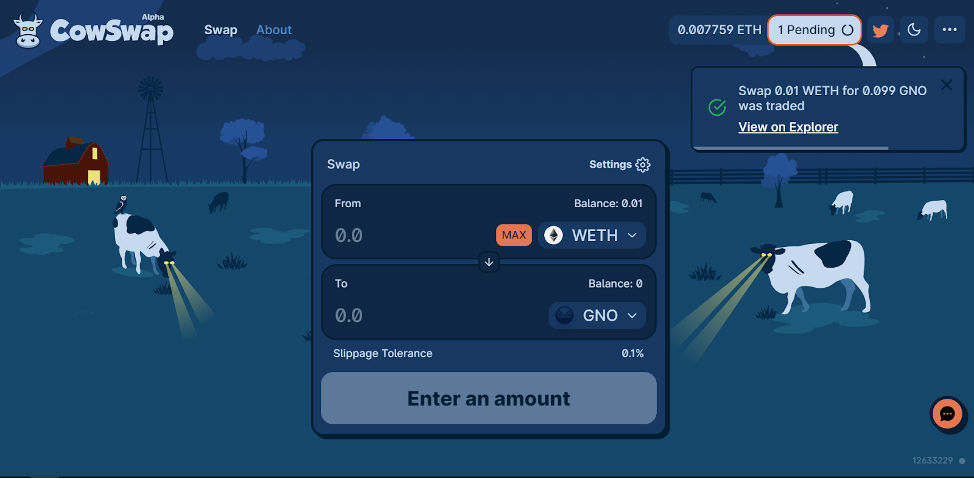
Each transaction is accompanied by the sound of cows’ mooing. Do not panic.
Conclusions
According to the Flashbots team, since January 2020 Ethereum arbitrage bots have earned almost $750 million from MEV.
Behind CowSwap’s playful interface lie the sophisticated technical solutions of Gnosis Protocol v2: the exchange protects users from MEV, optimises gas costs, and enables trades at prices better than the market through a combination of CoWs and Gas-Free Transactions with DEX-aggregator features.
Follow ForkLog news on Twitter!
Рассылки ForkLog: держите руку на пульсе биткоин-индустрии!


