
Scammers Target Aave Users Through Google Ads
Cybercriminals have launched a phishing campaign targeting Aave users via Google Ads, according to cybersecurity experts at PeckShield.
#PeckShieldAlert Fake “Aave” ads are topping Google search results.
The phishing site is aaxe[.]co[.]com.
The ads are designed to drain your wallet through malicious transaction signatures. pic.twitter.com/LdVHMflFAT
— PeckShieldAlert (@PeckShieldAlert) August 7, 2025
The perpetrators placed paid advertisements on Google Ads, mimicking the official Aave platform. Clicking the links redirected victims to fake websites where they were asked to connect their crypto wallets. This allowed the scammers to gain access to the funds.
Such transactions are irreversible. The exact amount of damage is still unknown. Users are advised to carefully verify website URLs. If a wallet is compromised, funds should be immediately transferred to a secure address, contact the provider through official channels, and revoke permissions using services like Revoke.cash.
Prior to reports of the phishing attack, Aave became the first DeFi protocol with a net deposit across 14 networks exceeding $60 billion.
$60B net deposits.
DeFi will win. pic.twitter.com/BsrEHbnji8
— Aave (@aave) August 6, 2025
According to Token Terminal, this figure has more than tripled over the year. In August 2024, it stood at $18 billion.
Fraudulent Campaign on YouTube
Meanwhile, experts at SentinelLABS reported another attack on crypto investors. Since 2024, criminals have been taking over old YouTube channels that previously published cryptocurrency news.
The scammers promote trading bots that steal users’ funds. Videos are created using AI, and negative comments are swiftly removed.
Victims are encouraged to deploy a smart contract that conceals the cybercriminals’ address. Once funded, the money is sent to the scammers’ wallets.
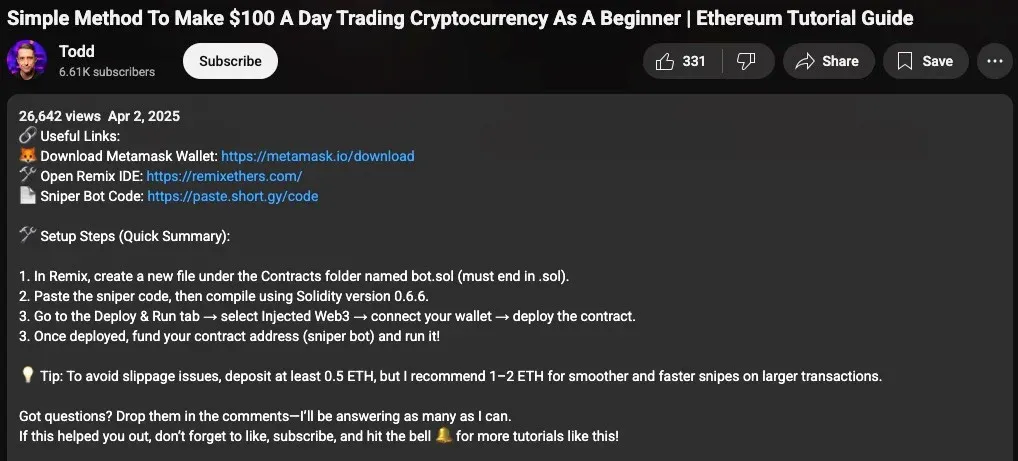
According to specialists, users are asked to deposit a minimum of 0.5 ETH (~$1829 at current rates) to launch the bot and cover fees. One fraudulent address has already received about 244.9 ETH, while two others have received 7.59 and 4.19 ETH. In total, this exceeds $939,000.
“We have observed the use of the same wallet in several malicious smart contracts. However, numerous unique addresses are involved, making it impossible to determine the exact number of scammers,” noted SentinelLABS.
Earlier, on August 6, a crypto investor lost $3 million by signing a malicious transaction. The phishing attack employed a common tactic: scammers create fake addresses or links that mimic legitimate ones.
Рассылки ForkLog: держите руку на пульсе биткоин-индустрии!


