What is Hedera Hashgraph (HBAR)?


Key points
- Hedera Hashgraph is a public network built on distributed-ledger technology (DLT), designed for businesses as a platform for decentralised services and applications.
- Hedera presents itself as a third-generation public network—the next stage after Bitcoin and Ethereum. Its strengths include high scalability, security, smart contracts, energy efficiency and low usage fees.
- Hedera Hashgraph is governed by a council of trusted companies responsible for software development and the platform’s overall direction. Members include Boeing, Swirlds, IBM, Nomura Holdings and Ubisoft.
- Hedera Hashgraph is built on an ABFT consensus algorithm underpinned by Proof-of-Stake (PoS). According to the developers, this provides strong security while keeping transactions fast and cheap.
Who created Hedera Hashgraph, and when?
The Hedera Hashgraph platform is based on the Hashgraph protocol, patented in 2016 by Swirlds. The design was developed by the firm’s CTO, Leemon Baird.
The first practical implementation came in 2017 as a shared enterprise network for the Credit Union National Association (CUNA) and the Mountain West Credit Union Association (MWCUA).
The public Hedera Hashgraph platform was founded by Swirlds co-founder Mance Harmon and Leemon Baird.
In 2018 Hedera Hashgraph raised $100m to develop the project. In 2019 the developers launched a public beta of the network.
Hedera Hashgraph’s investors
The Hedera Hashgraph platform has the backing of several large investors:
- Digital Currency Group (DCG), the parent of digital-asset manager Grayscale Investments. DCG has invested in many well-known industry players, including Coinbase, Kraken, Coinlist, Zcash, Ripple, Ledger and Decentraland;
- Fenbushi Digital, one of China’s oldest and best-known venture firms. Until 2018 its general partner was Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin. The firm has participated in funding rounds for The Graph, 1inch Network and Nym Technologies;
- Multicoin Capital, a crypto investment company founded in 2017. Multicoin Capital led one of the early funding rounds for Solana Labs and invested in the FTX exchange. In July 2022 the company announced a $430m venture crypto fund.
Who governs Hedera Hashgraph?
The platform is governed by the Hedera Governing Council, formed in 2019 from several representatives of the Fortune 500.
As of late July 2022, the council had 26 companies and organisations, including Boeing, Swirlds, IBM, Nomura Holdings and Ubisoft. Membership is capped at 39. Terms last three years with the possibility of two renewals.
The council is tasked with safeguarding the codebase and mitigating the risk of a hard fork. It also sets membership policy, establishes network rules, manages the platform’s treasury and approves technical changes.
Because Hashgraph is patented, unauthorised use of Hedera’s code entails legal action. According to the project team’s statement, this means the network cannot be copied and launched by other crypto-market participants.
That differs markedly from Bitcoin—anyone can use the first cryptocurrency’s blockchain code and modify it at will.
How does Hedera Hashgraph work?
The Hedera Hashgraph distributed network uses a data structure different from a blockchain: a directed acyclic graph (DAG). In a DAG, batches of transactions and other data are not chained in strict linear order as in Bitcoin; they are recorded to the ledger regardless of sequence.
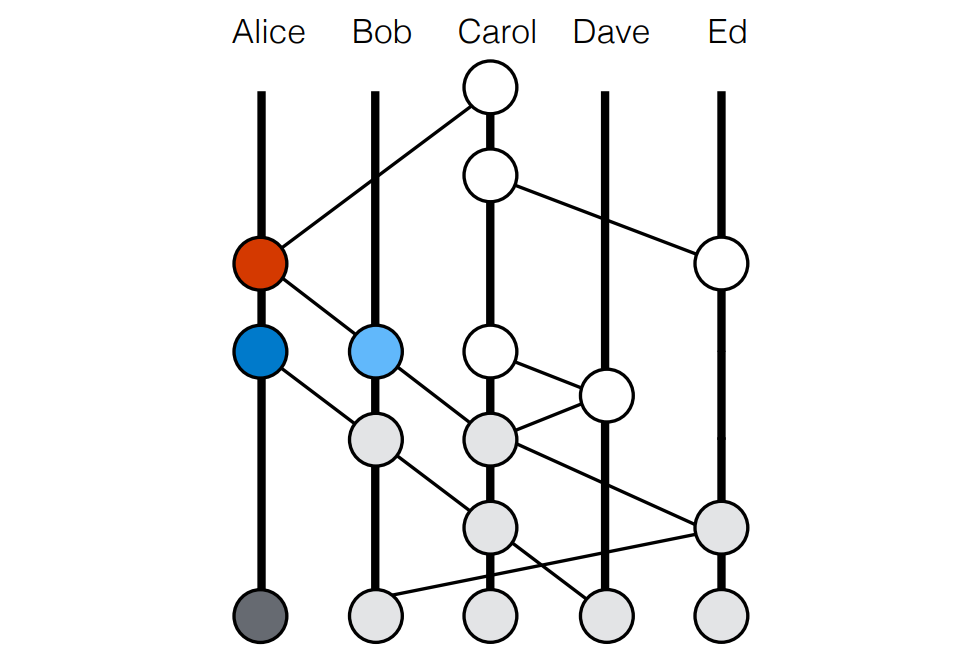
In blockchains, miners compete to process the same transactions and tasks, in a sense wasting energy. By contrast, a DAG architecture allows many independent, parallel computations, which increases throughput and energy efficiency.
Hedera Hashgraph also relies on several other mechanisms.
Asynchronous Byzantine fault tolerance (ABFT)
ABFT is an implementation of the Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) consensus algorithm used in blockchains such as Cosmos and Solana. It protects the network against malicious behaviour by up to one-third of nodes.
Gossip protocol
In Hedera, gossip is used to exchange messages (transaction, timestamp, signature) between nodes. A node sends a message to its neighbours, which pass it on to their neighbours, and so on until the information reaches all participants.
This helps preserve bandwidth when transmitting data. The same “conversation” mechanism is used by Theta Network and IOTA.
Proof-of-Stake
Staking in Hedera Hashgraph differs from the mechanism in Ethereum 2.0 and other PoS blockchains, where each node votes for a block.
Instead, nodes determine mathematically which block the next node will vote for—a system called “virtual voting”. Even if a malicious node works against the rules, the honest participants’ computations prevent an incorrect decision.
How is Hedera Hashgraph used?
The developers position the project as a platform for business, so the network has several specific features. Unlike Ethereum and BNB Chain, an ordinary user cannot deploy a smart contract or decentralised application.
To gain full access to Hedera’s services, you must create an account and complete verification. After verification, the following become available:
- issuance and management of tokens, including NFTs;
- creation and deployment of smart contracts in Solidity and Vyper;
- file-service operations—storing, verifying, viewing and managing credentials and other information on the network.
This approach helps protect the platform from fraud and ensures compliance with the requirements of specific participants in given jurisdictions.
Through intermediaries such as exchanges and authorised wallets, Hedera Hashgraph allows “ordinary” accounts without verification. The current list is available on the website of the project.
Features of Hedera Hashgraph
Hedera’s source code is closed and protected by a Swirlds patent. Members of the Hedera Governing Council are responsible for the platform’s governance and development.
According to the developers, Hedera Hashgraph is an enterprise-grade platform with limited user access to the network and to development on top of it. It is one of the few crypto projects initially focused on regulatory compliance.
Despite its restrictions, Hedera Hashgraph has several competitive advantages highlighted by the team:
- Speed and scalability. As of July 2022 the platform can process more than 10,000 transactions per second, with further scaling possible via sharding.
- Low fees. Transaction fees are fractions of a cent, a clear advantage over rivals such as Ethereum and BNB Chain.
- Low energy consumption. The network does not require energy-intensive computations as in Proof-of-Work systems. According to the project, Hedera consumes just 0.00017 kWh, which is hundreds of thousands of times less than Bitcoin’s blockchain.
- Legal compliance. Hedera is oriented toward complying with laws in various jurisdictions by imposing restrictions on users and locations. According to the Hedera FAQ, full access is unavailable to users from nine regions: Belarus, Crimea, Cuba, Iran, Japan, North Korea, Syria, Sudan and Ukraine.
Рассылки ForkLog: держите руку на пульсе биткоин-индустрии!


