
Researcher Outlines Plans for Transforming Ethereum Transactions
Ethereum undergoes a "quiet yet fundamental transformation" in block verification.
The Ethereum network is undergoing a “quiet yet fundamental transformation” in its block verification process, according to a statement by an Ethereum Foundation member known as ladislaus.
“Whether you are a scaling advocate, an individual staker, a home validator, or a self-checking enthusiast — this will matter to you,” the researcher noted.
He explained that Ethereum is shifting from re-executing all transactions on nodes to verifying the correctness of operations through zkEVM proofs.
Currently, each node in the network wishing to validate a block must re-execute every transaction within it, leading to multiple repetitions of the same actions across nodes.
The workload of validators is tied to the gas limit — the higher it is, the greater the bandwidth requirements for the operator.
However, ladislaus envisions a different solution: instead of repeating computations, a node verifies a cryptographic proof of the action’s correctness.
“This is what zkEVM proofs provide — a path to significant L1 execution scaling in the long term,” added the Ethereum Foundation member.
The concept is not new, but its refined essence now integrates into the core Ethereum protocol not as an aggregation function, but as an optional step in the consensus-level verification process.
How It Works
Network developers plan to create a so-called “proof pipeline.” ladislaus described its mechanism:
- The execution layer (EL) client generates an ExecutionWitness — a “self-sufficient” data package necessary for block verification without storing the full state.
- A standardized guest program uses this base to verify the state transition. The zkVM executes the request, and the validator generates a proof of correctness.
- The consensus layer (CL) client verifies this proof.
This will introduce a new category of network participants — zkAttesters. These are CL clients that verify zkEVM proofs instead of running a full EL.
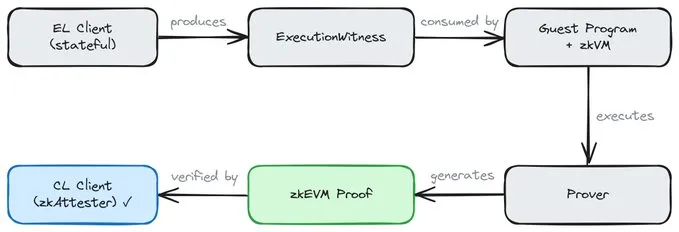
“Synchronization boils down to downloading proofs for the latest blocks since the last finalization checkpoint,” ladislaus explained.
Currently, a validator’s work involves simultaneously running both CL and EL clients, with the latter being particularly resource-intensive. State storage, block processing time, and bandwidth all increase proportionally to the gas limit.
According to the researcher, replacing re-execution with proof verification could significantly reduce hardware requirements for consensus participation.
“Perhaps the greatest benefit will be for individual stakers and home validators. As zkAttesters, they will no longer need to run a full EL test and can synchronize data in minutes. Proof verification replaces re-execution, thereby reducing hardware requirements,” he suggested.
The proposed changes are planned for implementation under EIP-8025, which is part of Ethereum’s roadmap for 2026.
Back in February, Vitalik Buterin outlined the future alliance of AI and Ethereum, emphasizing the need to pursue a positive path.
Рассылки ForkLog: держите руку на пульсе биткоин-индустрии!


