
The Illusion of Thought: Apple’s Study Reveals AI’s Limitations in Complex Problem Solving
Researchers at Apple have discovered that even the most advanced language models with “reasoning” capabilities (LRM) are unable to solve tasks in a generalized manner. Their logical abilities are limited and, in some cases, illusory.
The team conducted an experiment to understand the real capabilities and limitations of models like OpenAI o1/o3, Claude 3.7 Sonnet Thinking, and DeepSeek-R1. These systems generate detailed chains of reasoning before providing an answer, which is supposed to enhance their performance.
Instead of standard mathematical tests, which can be “contaminated” by internet data, the team used controlled puzzles. These included the Tower of Hanoi, River Crossing, and Block World. This approach allowed for precise measurement of task complexity by changing the number of elements and analyzing not only the final answer but also the entire “thinking” process of the model.
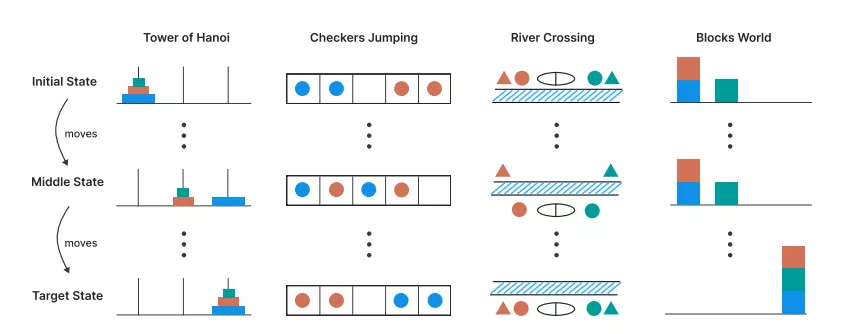
Collapse at High Complexity
The main finding of the study is that the performance of all modern LRM models drops to zero once the puzzle complexity exceeds a certain threshold.
The effort in “thinking,” measured by the number of tokens used, increases with task complexity, but only up to a point. Before a complete failure, the model paradoxically begins to “think” less, even though it has sufficient computational resources to generate a lengthy answer. This indicates a fundamental limit to scaling their logical capabilities.
Three Performance Modes
By comparing “thinking” models with their standard versions (LLM), researchers identified three modes of operation depending on task complexity:
- low complexity — LLMs without reasoning functions perform better and more efficiently;
- medium — LRMs demonstrated an advantage due to their chains of reasoning;
- high complexity — both types of models completely failed the tasks.
Inability to Follow an Algorithm
Researchers provided the model with an exact algorithm for solving the Tower of Hanoi, which required only the sequential execution of steps. However, it still failed at the same level of complexity as when searching for a solution independently. This calls into question their ability to perform precise calculations and logic.
The authors concluded that current LRMs, despite their complex mechanisms of self-reflection, do not possess generalizable problem-solving skills. Their successes may be more related to advanced pattern matching rather than actual reasoning, making the term “illusion of thinking” from the study’s title quite accurate.
In May, the OKX exchange released a report stating that artificial intelligence and blockchain are opening new approaches to generating income in various industries.
Рассылки ForkLog: держите руку на пульсе биткоин-индустрии!


