What are fiat currencies?


Key points
- Fiat money is fiduciary—based on trust—state-issued currency not backed by any asset or physical commodity and lacking intrinsic value.
- The bedrock of fiat money is users’ and holders’ confidence in the issuer, the state. The value of fiat money is determined by the quality of governance and the performance of the national economy.
- Fiat money replaced gold-backed currencies. Under the gold standard, banknotes and other obligations of a sovereign state were backed by a standardised quantity of precious metal.
- Issuance and the regulation of money in open markets and the wider economy are controlled by the state according to the country’s financial conditions.
History of fiat money
The first attempt to introduce fiat is recorded in the third century. Roman emperor Diocletian legally fixed coin values above the nominal price of the silver they contained.
The first fiat money close to modern forms is considered to be the currency introduced under China’s Tang dynasty in the eighth century. Issuance aimed to curb inflation and private coinage and to strengthen state control over finance.
The modern financial system and fiat money emerged after the end of the US dollar’s peg to gold in 1971. The United States unilaterally stopped exchanging the precious metal at a fixed rate and set in motion the “printing” of unbacked currencies worldwide.
The reason for abandoning the gold standard in the United States was a prolonged trade-deficit problem and a mismatch between the dollar’s exchange rate and its real purchasing power.
The gold standard as a generally accepted backing for state currencies ceased to exist in 1973 at the Jamaica international conference. Since then, exchange rates on the international market have been set by supply and demand.
Advantages of fiat money
Ending the gold standard gave governments access to unlimited money issuance. There is no need to replenish treasury reserves with gold or other hard commodities—currency printing can be aligned with any events, plans or goals.
This allows the state to channel investment in the form of cheap credit to any consumer groups, spurring production and demand and thus improving the efficiency of the economy as a whole.
The main tool of economic support has been quantitative easing (QE). QE injects additional liquidity into markets by having the state buy assets from banks and other financial institutions.
QE aims to expand money reserves in the economy to loosen monetary policy: cutting refinancing rates for banks, easing consumer access to cheaper loans, reducing systemic risks and improving the investment climate.
Drawbacks of fiat money
Flexibility and freedom in monetary policy can be a boon, but they can also create problems. Key risks include:
No intrinsic value
The loss of trust—the fundamental basis of fiat money—can wipe out the value of investments and savings, up to a full halt of the economy.
Political risk
The value of a particular fiat currency depends on the effectiveness of state governance. Past stability does not guarantee future stability owing to political risks at home and abroad.
Examples include the 1998 crisis in Russia and the volatility of the rouble after the war with Ukraine began.
Debt spiral
Government access to virtually limitless issuance brings the risk of creating vast amounts of unsecured debt. The United States is an example. The country has one of the world’s most developed economies and, at the same time, the largest debt, which in the first quarter of 2022 exceeded $30trn, or 133% of GDP.
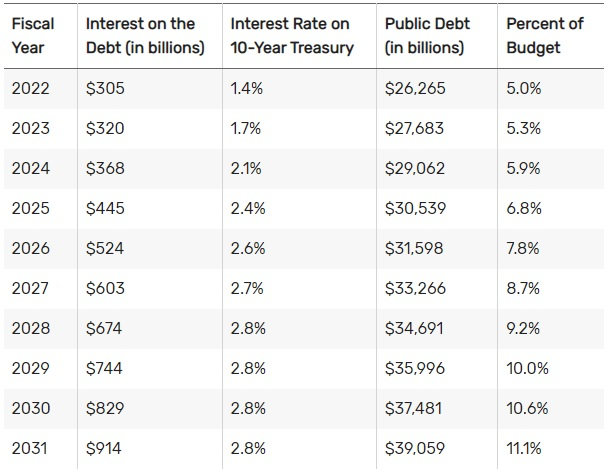
According to the US Treasury, annual interest on the debt accrued by June 30, 2022 amounted to 5% of the federal budget for the same period. The US budget deficit for 2022 was $1trn—the gap is covered by issuing and selling bonds.
According to the Congressional Budget Office, by 2031 interest payments alone will amount to $914bn. The US government does not have enough money to meet these obligations and is forced to create new debt to pay the old.
Financial bubbles
A vivid example of inefficiency in a fiat-based economy is the 2006 US housing bubble, which led to the 2007–2008 financial crisis.
Banks channelled capital by creating artificial demand for housing. They originated loans and resold these obligations to other banks in the form of derivatives. Once borrowers stopped paying interest and property prices stopped rising, the market collapsed like dominoes.
Cryptocurrencies: an alternative to fiat money
Commodity-backed currencies are not the only alternative to fiat. The cryptocurrency industry, as a young participant in global finance, can foster more efficient economic models.
No restrictions
Cryptocurrencies are based on distributed-ledger technologies, including blockchains and the directed acyclic-graph concept. With internet access, anyone can join public crypto networks without restrictions of jurisdiction, age, time zone, gender, financial status or political affiliation.
Decentralisation
Cryptocurrencies are designed around decentralisation: no one should hold a dominant vote; changes to the system are made through public consensus.
Issuance mechanism
Issuance mechanisms are set before a network or token launches. Every participant knows in advance how many units (tokens, coins) will be created or destroyed and under what conditions.
No intermediaries
To send cryptocurrency to someone next door or on the other side of the globe, no intermediaries are needed—only the recipient’s address and a small transaction fee.
To swap one cryptocurrency for another, there are special decentralised exchanges and swap services that operate autonomously from anywhere in the world—DEX.
Further reading
Where to track cryptocurrency prices?
What is dollar-cost averaging?
Рассылки ForkLog: держите руку на пульсе биткоин-индустрии!


