Aptos: the next generation of blockchain platforms?


Key points
- Aptos is a blockchain platform built on the AptosBFT consensus algorithm. It uses the bespoke Move programming language to create smart contracts.
- The project was founded by former staff of Diem (formerly Libra), Meta’s blockchain that was shut down in early 2022. Move was originally developed for Diem.
- Developers say parallel execution enables Aptos to reach over 160,000 transactions per second.
- In 2022 the team raised $350m. The Aptos blockchain is in its final testing phase, with mainnet planned for launch by end‑2022.
Project history
The project is led by former Meta employees who had worked since 2018 on Libra, later renamed to Diem in 2020. Meta planned to integrate the Diem blockchain and cryptocurrency into Facebook, Instagram and WhatsApp. The project, however, collapsed under regulatory pressure. In February 2022 it was sold to Silvergate Capital Corporation, reportedly for $200m.
Soon after, former Meta partnerships lead Mo Shaikh and blockchain engineering head Avery Ching founded Aptos Labs. Many others who had worked on Diem also joined the Aptos team.
In 2022 the Aptos blockchain project raised $350m across two funding rounds. The March 2022 seed round totalled $200m, led by Andreessen Horowitz with participation from Multicoin Capital, Coinbase Ventures, Tiger Global, FTX Ventures, Paxos and others. The $150m Series A in July 2022 was led by FTX Ventures and Jump Crypto. In September 2022 Binance Labs invested in Aptos; the amount was not disclosed.
Aptos is currently undergoing several testing phases, and no firm mainnet date has been named. Token Insight, citing the project’s Discord, reported it should happen by 22 December 2022 (the post was later deleted).
How testing works
Public testing of the Aptos network began in May 2022. According to the roadmap, it is split into several stages with specific goals:
- Aptos Incentivized Testnet 1 (AIT1). Registration of initial participants, launch of a limited node network, and validator documentation. Completed in June.
- AIT2. Testing staking mechanisms and validator incentives via “decentralised faucets”. Completed in August.
- AIT3. Introduced on‑chain voting and mechanisms to onboard new validators. Successfully completed in mid‑September.
- AIT4. Stress‑testing validators ahead of mainnet. Started in mid‑September 2022.
At each stage, participants were offered rewards in test Aptos tokens for completing set tasks. After launch, they will be exchanged for the project’s cryptocurrency issued on mainnet. Detailed technical documentation is available for anyone wishing to take part in testing.
Features of the Aptos blockchain
Aptos is designed as a flexible, easily upgradable platform for the ever‑shifting Web3 landscape. As the developers state in the project’s whitepaper, Aptos combines consensus, a new smart‑contract design, security, performance and decentralisation in a novel way.
User, application and smart‑contract interactions are powered by the Move VM, which aims to challenge the “monopoly” of the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). By the account of the Pontem team developing Move, Aptos’s virtual machine could become a standard for integrating applications from Cosmos, Solana, Polkadot and even Ethereum.
The Aptos blockchain uses the AptosBFT consensus algorithm, based on HotStuff—an implementation of Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) created specifically for Diem.
BFT provides strong protection against malicious behaviour, allowing the network to function even if a third of validators are compromised or fail. This consensus mechanism is also used by blockchains such as Hedera Hashgraph, Cosmos, Solana and Everscale.
According to Aptos Labs engineer Joshua Lind, test results showed that, thanks to modular design and parallel execution, Aptos can process over 100,000 transactions per second (TPS) without sacrificing security or decentralisation. Transaction finality—ie, the time between submission and execution—is under one second.
Aptos architecture
The Aptos network has not been officially launched and, at the time of writing, remains in testing. For that reason, the advantages described in the technical documentation cannot yet be validated by empirical data. Even so, the key points are:
- The Move programming language is suited to fast, safe transaction execution, allowing developers to better protect their software from malicious code;
- Flexible private‑key management and pre‑execution transaction previews offer a better user experience;
- High throughput and low latency are enabled by parallel transaction processing—Block‑STM. By the team’s estimates, it can push Aptos’s performance beyond 160,000 TPS.
- Aptos’s modularity allows the blockchain to be segmented for rapid deployment of applications and new Web3 use cases. It also enables testing and protocol‑level upgrades without halting the network.
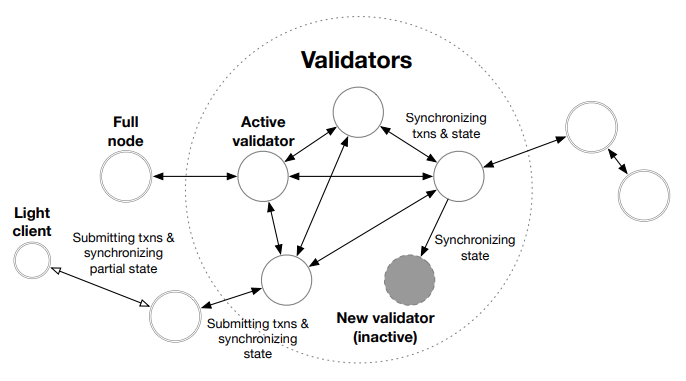
The architecture of Aptos envisages participation at different levels and with distinct roles to ensure integrity:
- Validators form the blockchain, confirming user transactions and producing blocks via the consensus process.
- Coin holders lock or delegate their funds to addresses of chosen validators.
- Clients are any components that submit transactions, request blockchain history or other data.
- Light clients maintain a limited set of current validators and can securely request partial blockchain state from full nodes.
- Full nodes are clients that replicate transaction and blockchain state from validators or other full nodes on the network.
The Aptos cryptocurrency
Aptos will have a native cryptocurrency of the same name. At the time of writing the Aptos blockchain has not launched, and no tokenomics have been disclosed. The Aptos documentation nonetheless lists several key uses for the coin:
- Transaction fees. As with other blockchains, the cryptocurrency will be used to pay transaction fees.
- Governance. APTOS will be used in voting on upgrades and other protocol‑governance matters.
- Staking. The Aptos cryptocurrency can be staked to earn additional income.
How the Aptos ecosystem is developing
One early initiative at the start of testing was close collaboration with Google Cloud in April 2022, which helped enable node deployment in 15 minutes in the cloud.
By late June 2022, more than 100 projects were being built in the Aptos ecosystem across popular sectors such as DeFi, NFTs and blockchain gaming. The Aptos team also highlighted developer communities contributing to the ecosystem: Pontem Network, Nutrios, PayMagic, MartianDAO, Solrise.
To bridge DeFi applications and improve the user experience in Web3, the LayerZero team announced integration of its cross‑chain protocol with the Aptos platform.
Scale3 Labs, a startup founded by former Coinbase specialists, announced plans to build infrastructure solutions for Aptos. The project aims to provide tools for uninterrupted operation by node operators.
Based on the available documentation, several applications are already being developed on Aptos:
- The decentralised exchange Liquidswap, developed by the Pontem team. The protocol will use a standard automated market‑maker (AMM) mechanism.
- The Blocto wallet will integrate the Aptos blockchain. Beyond storage and transfers, staking of the project’s cryptocurrency will also be available.
- In liquid staking, two applications are active—Ditto and Tortuga Finance.
- For NFTs, the marketplace is Topaz.
- The Aptos Launcher platform, built using smart contracts, is designed for crowdfunding projects on Aptos.
Further reading
What is a DAO (decentralised autonomous organisation)?
The Proof‑of‑Stake (PoS) consensus algorithm: how does it work and why is it so popular?
What are sidechains and how do they work?
Flow blockchain and cryptocurrency: a review of the L1 platform for NFTs and GameFi
Рассылки ForkLog: держите руку на пульсе биткоин-индустрии!


