
DeFi 2.0: How next-generation decentralized protocols are evolving
DeFi is continually evolving. Beginning the year at about $21.55 billion in total TVL, it has risen more than tenfold, reaching $270 billion by mid-November.
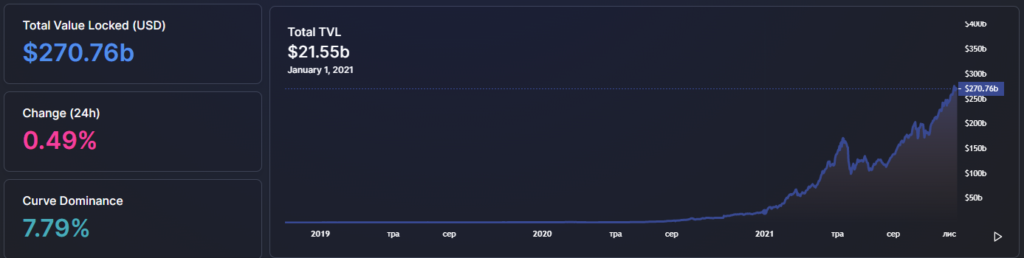
The remarkable rise has been propelled by the daily emergence of new projects offering—especially at the outset—high yields on invested capital, as well as attractive liquidity-mining programs.
Second-layer solutions and new L1 protocols are making transactions faster and cheaper, while cross-chain bridges enable the safe movement of funds across different networks. All of these innovations contribute to higher liquidity and motivate developers to create new financial products.
Many next-generation services are aimed at addressing the shortcomings of popular non-custodial platforms, which have manifested in a steady decline in profitability metrics and user attrition. Beyond capital efficiency, they are oriented toward long-term goals, including price stability of the native token and the building of cohesive communities.
ForkLog has taken a close look at the features of DeFi 2.0 projects that radically rethink approaches to liquidity management.
Key takeaways
- Liquidity mining is a controversial approach, contributing to market saturation with an excess supply of devalued tokens.
- Liquidity mining programs popular among DeFi protocols often yield only a short-term effect—users quickly sell the tokens they receive.
- Decentralized next-generation services are emerging and developing—DeFi 2.0.
- These projects frequently employ the concept of protocol-controlled liquidity, aimed at the sustainable development of the ecosystem.
Disadvantages of liquidity mining and the DeFi 2.0 concept
The main problem of DeFi projects lies not so much in attracting liquidity as in retaining it in the medium- and long-term.
Many platforms distribute generous rewards in the form of native tokens—via airdrops and liquidity mining. This allows capital to be attracted in the short term, reflected in TVL growth.
However this approach does not guarantee user loyalty—after such programs finish, many market participants move to new platforms offering more attractive APY or conduct airdrops.
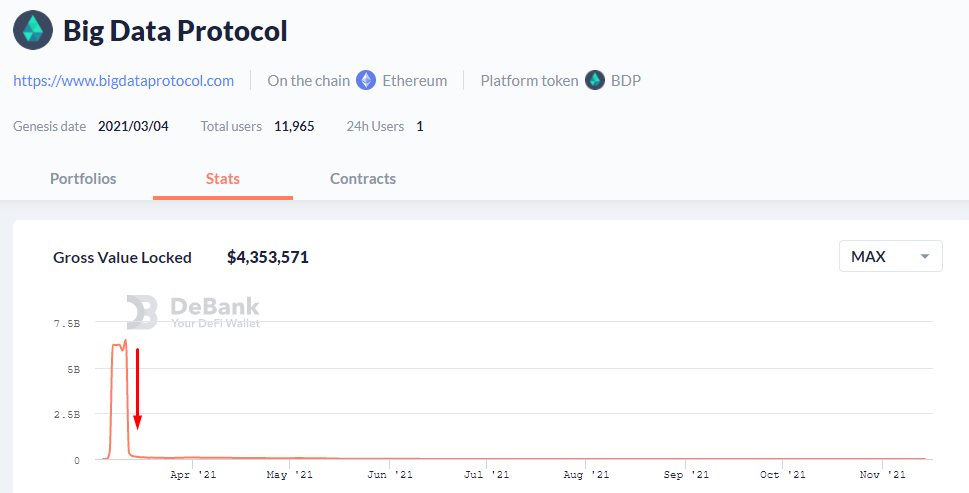
As a result, the price of the native token, often linked to the quality of the project itself, comes under selling pressure. For example, the Big Data Protocol reached a TVL of $6 billion during a six-day liquidity-mining program, but soon after the program ended the metric fell sharply. At the time of writing, TVL stood at only $4.3 million.
Economist Alex Kruger concluded that tokens minted within liquidity mining programs are often used inefficiently—most investors seek to dispose of them quickly.
He analyzed on-chain data for the 100 largest holders of the governance token COMP from Compound. In his observations, 809,000 coins worth more than $270 million (69% of the token’s circulating supply) flowed to these addresses.
“However, very few of them are COMP hodlers. Only 19% retained more than 1% of the COMP tokens, and only 7% kept more than 50% of the received amount. Do mining-reward holders maintain an economic interest in the Compound protocol? No,” Kruger emphasised.
Some projects attempt to solve or at least soften the problem with vesting. However, this often yields only a temporary effect, slowing the price decline.
To solve the issue, some protocols resort to fairly intricate models designed to retain liquidity and ensure price stability of the native token.
The following DeFi 2.0 concepts are experimenting with tokenomics and implementing unconventional approaches to attract and sustain user funds, enhance capital efficiency and reduce transaction costs.
OlympusDAO
One of the best-known examples of next-generation projects. The launch took place in March 2021. The key element of the project is the algorithmic OHM token, positioned as a decentralized reserve currency.
OlympusDAO sells OHM to users at a discount, receiving in return stablecoins such as DAI, FRAX, LUSD and liquidity-provider (LP) tokens based on the project’s native asset. For example, a user can acquire OHM with LP tokens of OHM-DAI, OHM-FRAX, OHM-WETH or OHM-LUSD.
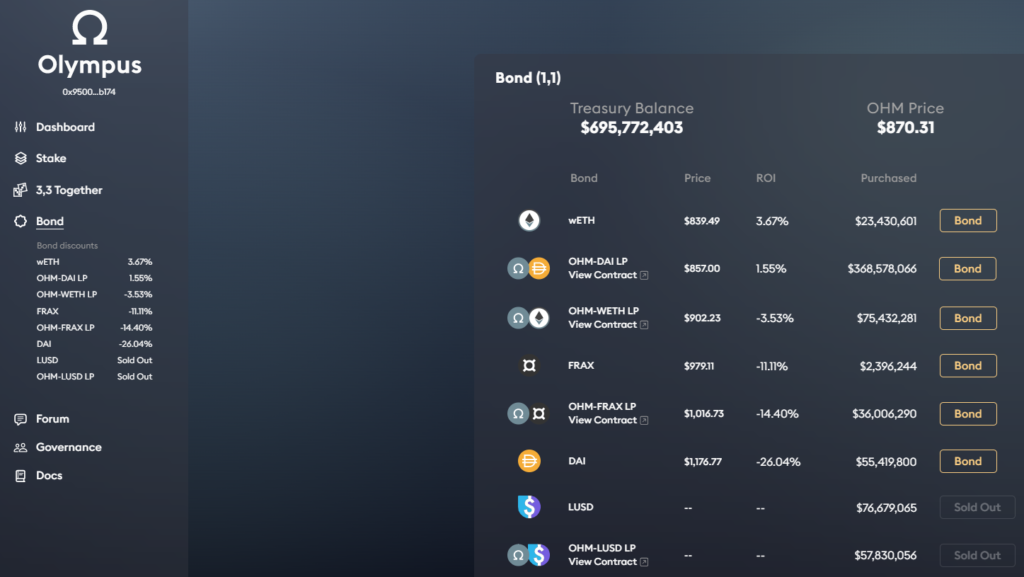
OlympusDAO aggregates its own liquidity using tools akin to discount bonds. Each OHM is backed by a basket of assets in the Olympus treasury. This, in turn, prevents the token price from falling below a defined price floor.
In protocol-controlled liquidity is the main distinction OlympusDAO from traditional DeFi projects. TVL of the latter dries up when the “perks” for users in the form of gradually devalued tokens run out.
Thanks to this unconventional model, the protocol controls almost 100% of the OHM-DAI liquidity, earning the corresponding commissions itself.

Users can also stake OHM, earning 7,997% per year (as of 14 November 2021).
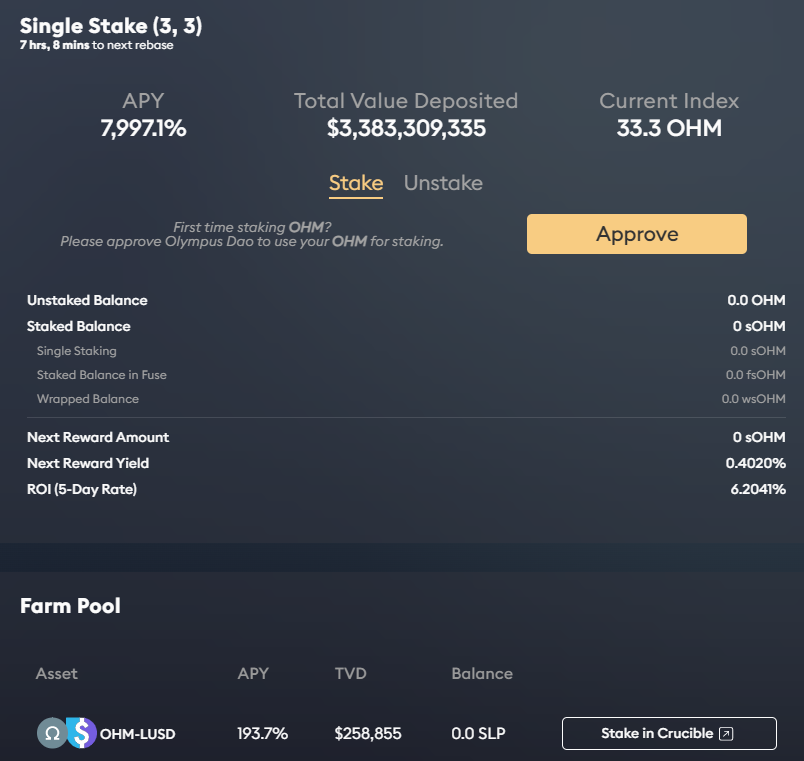
Staking counters buying pressure on the native token’s price.
Thanks to a high APY, more than 90% of the OHM supply is staked.
Market capitalisation of OHM reached $1.45 billion, and the project’s TVL stood at $783 million (as of 14 November 2021). And all this without liquidity mining or other incentive tools.
The project recently launched Olympus Pro, intended to become “the new industry standard among platforms helping protocols acquire their own liquidity.”
According to the documentation, the platform operates on a model bonds-as-a-service, solving for projects’ funding needs at a small fee. Olympus Pro is used by Alchemix, Frax, StakeDAO, Pendle, BarnBridge, Scream, Spooky Finance and PoolTogether.
Tokemak
Developers of Tokemak have applied their own approach to protocol-controlled liquidity, using a decentralized market-making mechanism.
Each asset on Tokemak has its own pools, called reactors. The project’s native token—TOKE— is used to govern liquidity.
A quick tour of the ecosystem’s core components.
Liquidity Providers (LPs). These market participants deposit assets into reactors and receive rewards in TOKE. The screenshot below shows projects participating in this program.
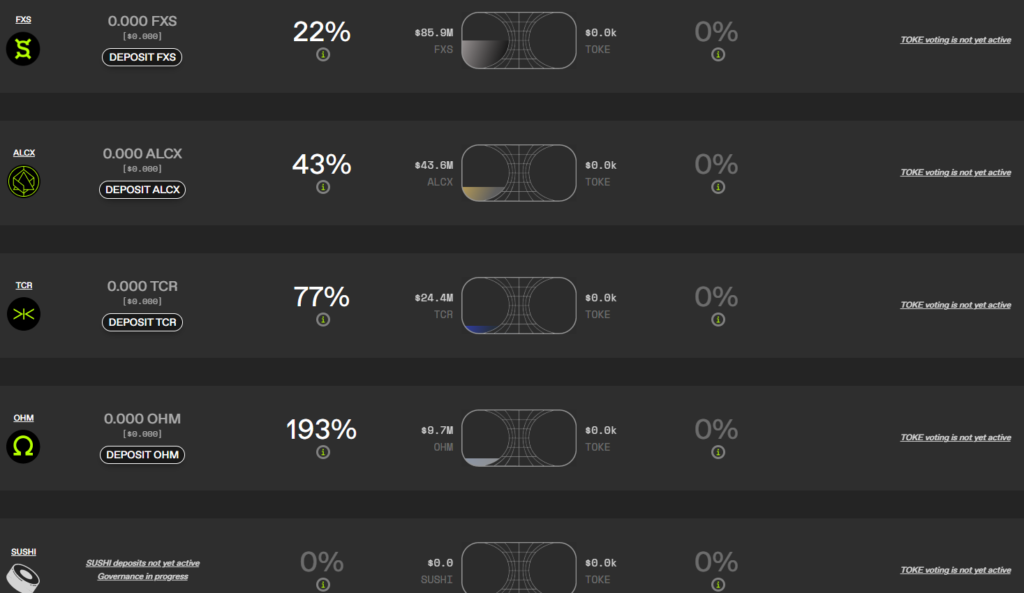
Assets obtained from LPs are then allocated as liquidity across various participating exchanges and currency pairs. A mechanism to mitigate impermanent loss is provided.
LPs can deposit highly liquid reserve assets like ETH and USDC, as well as the tokens of projects using Tokemak.
Liquidity Directors (LDs) stake the TOKE governance tokens, which function as tokenized liquidity. In addition to the yield, they gain the right to decide where to direct the LPs’ liquidity.
Pricers provide real-time market data to set bid and ask prices.
t-assets. When LPs deposit funds into a reactor, they receive a corresponding amount of t-assets. The latter are burned when users retrieve their base tokens.
The platform, according to co-founder Carson Ku, is a “network that generates sustainable liquidity for new and existing DeFi protocols.”
Tokemak earns revenue from trading commissions on the exchanges where liquidity is routed. These inflows are accumulated in the project’s treasury, acting as protocol-controlled liquidity.
Liquid staking
An innovative staking approach is offered by Osmosis—the AMM‑exchange in the Cosmos ecosystem.
Users place funds in pools with the OSMO token. However, beyond liquidity provision rewards, there is also the possibility to earn income from staking.
Suppose the yield from funds placed in an ATOM-OSMO pool, as well as from staking OSMO, is 100%. Placing $1000 in the pool would yield a daily income of $2.70 (at a rate of 0.27%). In addition, a daily $1.35 would accrue on a $500 OSMO stake. Thus, total daily income would amount to $4.05.
Protocols for managing tokenized assets
With the growth of the DeFi ecosystem, platforms such as Tranchess have emerged, offering structured products for investors with different risk appetites.
Users can earn income in Chess tokens by staking highly liquid assets—Bitcoin, Ethereum and USDC.
The platform is built on Binance Smart Chain (BSC). To earn income, for example from the first cryptocurrency, a Web3 wallet such as MetaMask is required, plus at least 0.01 BTCB.
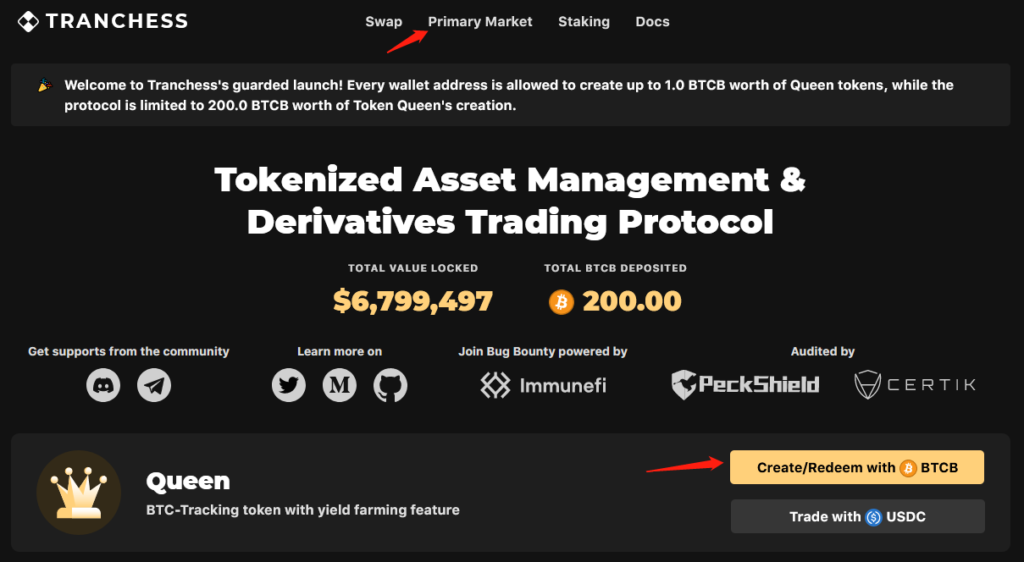
Clicking on Primary Market or Create/Redeem with BTCB takes the user to the Create/Redeem page. Then click Approve BTCB to authorize the use of wrapped Bitcoin. Before that, ensure there is some BNB in the wallet to cover network fees.
After confirming the transaction, enter the required amount in BTCB and click Create.
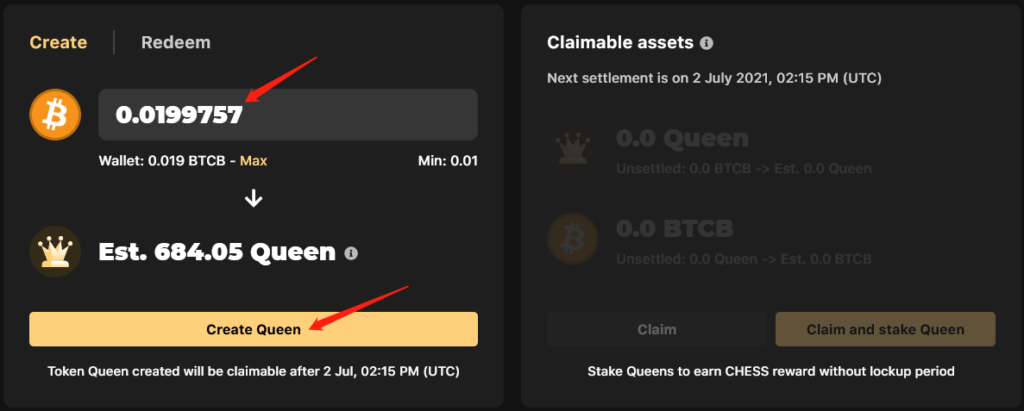
Over time, a certain amount of bQueen tokens will be generated. They can then be claimed to the wallet by clicking Claim.
If you select Claim and stake bQueen, the process of farming the governance token Chess begins. The latter can also be purchased on external platforms such as Binance and PancakeSwap and locked on Tranchess to increase earnings.
Tokens bQueen can also be bought on the built-in marketplace for USDC. There is an option to split them into other platform assets — BISHOP and ROOK — and to reassemble them back into bQueen.
Similarly, you can farm Chess using Ethereum, generating eQueen tokens.
Investors in Tranchess include Three Arrows Capital, Spartan, Binance Labs, IMO Ventures and LongHash Ventures. The protocol was audited by PeckShield and Certik.
Tranchess ranks third in TVL among BSC projects, at $1.6 billion (DeFi Llama data as of 15 November 2021).
Second-order protocols
This category includes over-the-top projects built on top of other protocols. These platforms are designed to:
- automate certain functions;
- increase yields, for example through compounding;
- expand the functionality of base platforms.
Let us look at some of the most popular second-order protocols.
Popsicle Finance. One of the platform’s key capabilities is managing concentrated-liquidity positions on Uniswap v3.
In early August a hacker exploited a bug in the Sorbetto Fragola project and drained assets worth more than $20 million. Soon after the incident, the project proposed issuing an NFT to compensate for hack losses, and by the end of October reported full reimbursement of losses with ICE tokens.
Another project — Convex Finance — is a decentralised staking service built on the Curve protocol. It lets liquidity providers boost staking yields without locking CRV tokens.
Pickle Finance helps users maximise returns from DeFi protocols by auto-compounding rewards. According to developers, the project saves users time and reduces gas costs. In addition to Ethereum, the platform supports the Polygon network.
A year ago the attacker withdrew nearly $20 million from one of Pickle Finance’s smart contracts. Shortly after the incident, the team announced a merger with DeFi project yEarn.Finance by Andre Cronje.
Considerable popularity has also come to the Autofarm. It is marketed as an aggregator of attractive farming opportunities across networks including Binance Smart Chain, HECO, Polygon, Avalanche and Fantom (the list of supported ecosystems is expanding). A key feature is automatic compounding “to optimise farming with minimal cost.”
One of the fastest-growing projects in recent months is Abracadabra. It employs a model of over-collateralized debt positions similar to MakerDAO. The difference is that Abracadabra users can earn income from collateral assets, including yvYFI, yvUSDT, yvUSDC and xSUSHI.
Instead of MakerDAO’s native stablecoin DAI, users of the new protocol issue the MIM (Magic Internet Money) token. As the value of collateral increases over time, the risk of liquidation diminishes.
Abracadabra also offers farming and staking of the native SPELL token. In addition to Ethereum, the platform operates on BSC, Fantom, Avalanche and Arbitrum.
A project similar in function to MakerDAO and Abracadabra is Alchemix Finance. The difference is that users’ debt positions are shielded from liquidations by issuing synthetic versions of the collateral asset. For example, a user deposits collateral in ETH or DAI and issues assets tied to their prices — alETH and alUSD respectively.
Alchemix Finance also offers asset swaps and farming.
Conclusions
DeFi is continually growing new capabilities, turning into a giant “financial LEGO.” The flip side is complexity for newcomers. Yet, given the industry’s already enormous yields, studying the technical details and investment opportunities of genuinely new protocols remains well worthwhile.
The relatively straightforward path—liquid staking—is also expanding. Besides Osmosis, this is implemented on the Persistence pSTAKE platform. The BENQI project on Avalanche is also working on its deployment.
Another promising direction is second-order protocols. But one should not forget that, like base platforms, such projects are also vulnerable to hacks. Popsicle Finance and Pickle Finance are examples.
In the future one can expect continued TVL growth and the further development of sophisticated DeFi solutions, as well as their integration with many new ecosystems and second-layer scaling solutions.
Subscribe to ForkLog’s news on Twitter!
Рассылки ForkLog: держите руку на пульсе биткоин-индустрии!


