
Five-Year Marathon: The Role of American Tech Giants in AI Development
Over the past five years, the AI market has boomed. Many companies and organisations are not only studying cutting-edge technology but also embedding AI tools into their day-to-day operations.
The major American tech companies, known as tech giants, have played a pivotal role in the sector’s development. Moreover, they spotted the direction’s potential early, and today they can be described as leaders in the AI market.
ForkLog has identified which companies are actively integrating artificial intelligence into their products and why they are investing tens of billions of dollars in the technology.
- The combined market capitalisation of the seven largest American tech giants accounts for almost half of the global IT sector.
- Powered by AI, the tech giants generate billions of dollars in revenue, allowing them to increase investments in the industry.
- American corporations face regulatory pressure and consumer criticism.
Who are the tech giants?
Tech giants are the large companies that dominate the technology market. They typically include Meta, Amazon, Apple, Microsoft and Alphabet. Nvidia is also included, and, recently, Tesla.
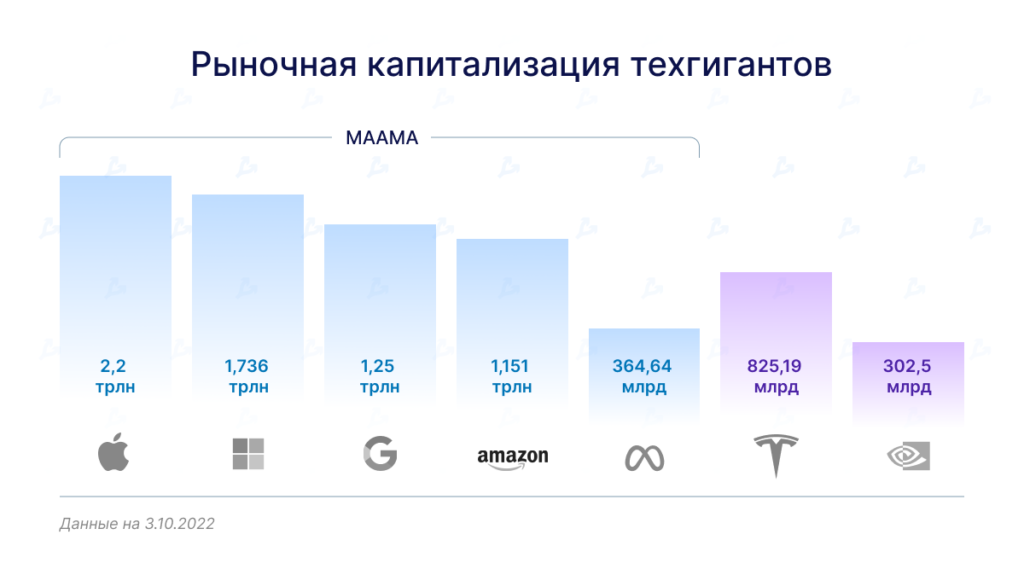
The combined market capitalisation of these seven companies stands at $7.84 trillion, or almost 48% of the global technology market. Collectively, American tech giants are worth as much as the other 842 public firms in the global IT sector.
The tech giants offer a wide range of services for consumer and enterprise markets. Key products include:
- software;
- enterprise hardware;
- consumer electronics;
- software development tools;
- cloud services;
- online advertising and sales tools;
- entertainment.
Often each tech giant occupies its own niche, but in some areas the companies are direct competitors: Google and Bing, Android and iOS, Windows and macOS, Apple MacBook and Microsoft Surface, and others.
The Path to AI for the Tech Giants
At first glance it may seem that the tech giants are not quite AI companies. Yet, each has for years embraced an AI-first approach, prioritising artificial intelligence technologies.
Alphabet was among the first to adopt such an approach. In 2017, the company’s CEO Sundar Pichai announced a shift from Mobile-First to AI-First.
“In the world of AI-First we are rethinking all of our products and applying machine learning and artificial intelligence to solve users’ problems. And we are doing this for every one of our products,” the Alphabet CEO said at I/O 2017.
Since then, the company has actively integrated AI features into products such as Search, Maps, YouTube, Pixel, Android and others.
Alphabet also develops cloud offerings, providing users with various AI tools for data analysis on its own infrastructure. In 2021, Google Cloud brought to the company $19.206 billion, or about 7% of total revenue. Practically all of the remaining revenue came from advertising.
Following Alphabet, Microsoft adopted the AI-First strategy. Today, the main source of the company’s revenue is Azure cloud services. They allow developers to use the company’s resources, including AI algorithms. Azure services provide capabilities in data analysis, computer vision, natural language processing and other areas.
For fiscal 2022, the Intelligent Cloud division brought $51.9 billion to the company — more than 26% of total revenue.
Amazon is not only the largest retailer in the US and Europe, but also a direct competitor of Microsoft and Alphabet in cloud computing. Amazon Web Services offers a wide range of services similar to Azure and Google Cloud. For the year 2021, the platform brought the company $62.2 billion in revenue.
Also, Amazon sells a range of AI-powered smart home devices within its ecosystem, including Echo Dot, the home robot Astro, and the Ring doorbell.
Since 2017, Apple has become more active in integrating AI into its products. This is evidenced by Apple Silicon chips (A-series and M-series), equipped with the dedicated Neural Engine for processing AI tasks. The company continually embeds AI features in the operating systems of its devices and in individual apps such as Camera or Apple Music.
Meta earns primarily from advertising on Facebook and Instagram. In addition, the company relies on content-recommendation algorithms, develops language models for translating text and captioning video, and releases the Quest virtual reality headset. The latter is intended to underpin the company’s future metaverse.
Nvidia is a leading maker of chips for the AI industry. Its GPUs with CUDA cores have revolutionised machine learning, making accelerators available tools for developers.
Nvidia’s product line includes dozens of AI accelerators, developer services, and components for large computing systems and supercomputers.
One of the company’s main lines of activity has become the production of chips for AI needs. Nvidia’s products are now used by other tech giants, data-centres, supercomputer manufacturers, autonomous vehicle developers and independent engineers.
Tesla shifted its focus toward AI in April 2021. In addition to popularising electric vehicles, the company is actively developing autonomous technologies, robots and its own supercomputer.
Over the past decade the automaker has achieved enormous success. According to CompaniesMarketCap, in 2012 the tech giant earned $410 million, and by 2021 $53.82 billion. It would seem the bet on AI is paying off.
The above revenues are largely indirect outcomes of AI. However, without it, the companies would unlikely have achieved such figures under their former business models.
A Quiet Expansion Through Investment
Investors and consumers focused on stock-market conditions often overlook projects that are not directly tied to core business lines or quarterly results. Yet research laboratories frequently generate products that extend beyond their initial objectives.
According to MacroTrends, tech giants’ R&D spending continued to rise in 2021.
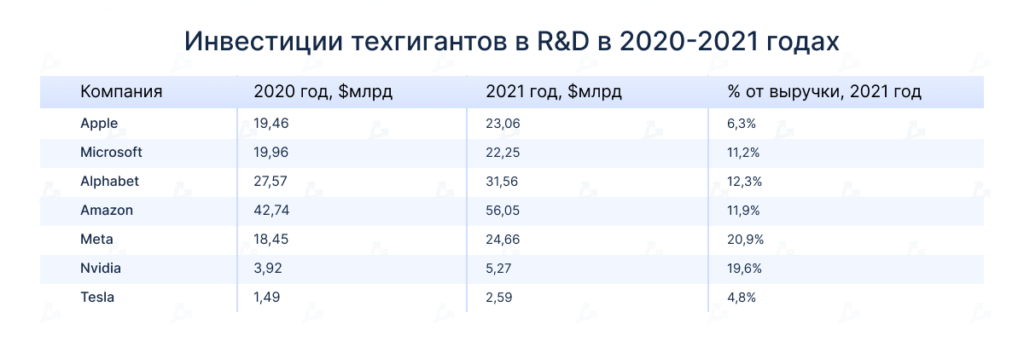
In 2021, the corporations allocated between 4.5% and 20.9% of revenue to R&D. By comparison, S&P 500 companies spent an average of 2.82% of revenue on R&D.
One of Meta’s latest strategic projects was a drive to scale computing power. As of early 2022, the supercomputer cluster numbered more than 6,800 Nvidia A100 accelerators. By the end of the year, Meta planned to raise the count to 16,000 units.
The computing power is intended to be used for speech processing and computer vision research, with a view to creating an immersive world the company calls the metaverse. This was disclosed by the project’s engineer-programmer Shubho Sengupta.
Alphabet’s AI lab DeepMind announced a system artificial-intelligence AlphaCode, designed to automatically write source code.
Researchers also developed new language model. This complements DeepMind’s claim of a breakthrough in understanding protein structures, which is crucial for drug discovery.
Apple has been working on at least two AI-related projects for years.
The first is an autonomous vehicle. According to Bloomberg journalist Mark Gurman, the company is actively developing a robo-car and plans to release it as early as 2025.
The other unannounced project is AR/VR glasses. According to Gurman, Apple was ready to unveil the device in 2022, but the coronavirus pandemic and supply-chain disruptions pushed plans back for an indefinite period.
According to the latest rumors, the company will release the headset in January 2023. Also, the tech giant registered the RealityOS trademark, indirectly indicating active development of headsets.
Microsoft invested $22.248 billion in R&D in 2021. Part of the company’s efforts is concentrated on partnerships with independent AI organisations, notably OpenAI.
In September 2020, the company entered into a partnership under which the tech giant gained exclusive rights to GPT-3, while the organisation used Azure’s power for its own research. A year earlier, Microsoft invested $1 billion in OpenAI.
Amazon, meanwhile, is looking to broaden its smart-home product line. In August 2022 the tech giant announced the purchase of robot-vacuum maker iRobot for $1.7 billion. The company believes it will strengthen its portfolio of projects.
However, critics opposed the acquisition. They argued the retailer intends to use robot vacuums to collect data on consumers’ homes to further intrude into their private lives and use that information to boost sales. The US Federal Trade Commission has already begun reviewing the deal, so a signed agreement in the coming year is unlikely.
The latest Nvidia conference took place under the banner of “Artificial Intelligence.” Virtually every product showcased by the company is aimed at developing various algorithms, from GeForce consumer GPUs with CUDA cores to the SaaS platform Omniverse.
In 2021, Nvidia’s total R&D investments dostigla $5.268 billion, or nearly 20% of annual revenue.
It is hard to predict the commercial applications of these studies. According to Kyun Hen Cho of New York University, in the short term we are unlikely to see any results. But strategically, the investments will eventually pay off.
“Such investments by leading technology companies… will spur and prompt other technology and non-technology sectors, for example, pharmaceuticals,” Cho said.
With great power comes great responsibility
A global concern for the tech giants is their monopolistic position in the market, which has drawn the attention of regulators in developed economies.
In the United States, calls have grown to curb Meta’s influence. The company is accused of unethical conduct, intentional use of algorithms to incite hatred, anti-competitive practices and more. The tech giant has also been criticised for censorship, misfiring moderation algorithms, and a heavy reliance on recommendation systems.
Recently, Mark Zuckerberg showcased what Horizon Worlds’ metaverse would look like. Users were dissatisfied with the platform’s graphics and did not believe the project was worth $10 billion.
Amazon, Microsoft and Alphabet have come under the attention of UK authorities. The country’s media and communications regulator intends to examine whether the firms comply with antitrust rules.
Apple has also come under regulatory pressure. Amid Epic Games’ lawsuit, regulators in the US, the UK, the EU and South Korea are seeking to force the company to lower App Store transaction fees. While the case is not AI-related, the situation could affect the tech giant’s finances and future investments.
Overall, the companies have found it harder to acquire small firms and rivals. As noted above, the Amazon-iRobot deal is under threat. Earlier this year pressure from the US, the UK, the EU and China scuppered Nvidia’s acquisition of Arm.
The latter faced another issue: export controls on AI technologies to China, which could cost the company hundreds of millions of dollars.
This is far from a complete list of regulatory probes against tech giants. Expect pressure to rise as the companies expand.
Beyond regulation, inflation, a 40-year high, has also affected the activity of the firms. One after another, the tech giants reported cost cuts and resource optimisation.
In July 2022, Meta’s product chief Chris Cox announced “difficult times” at the company, linked to privacy policy changes and macroeconomic pressures. In conversations with staff, he spoke of slower hiring of new engineers and budget cuts.
The same goes for Alphabet. CEO Sundar Pichai said it should run “20% more efficiently” and announced a hiring freeze.
On the eve of new iPhone releases, rumours swirled that Apple would raise iPhone prices. Later it turned out prices stayed at last year’s level for the US and Chinese markets; in other key countries smartphones did rise in price.
Raising prices also affected Nvidia products. Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang explained that Moore’s Law is no longer a guiding principle and processors will become more expensive.
There is another problem in AI: a shortage of computing power. Despite progress in chip-making, moving to the 3nm process and developing dedicated AI accelerators, current systems cannot provide the resources needed to build large models. Development and training of algorithms are becoming more complex, and data volumes continue to grow.
The AI industry faces a talent shortage. According to Glassdoor, demand for AI specialists is set to rise in the coming years. Yet the market cannot keep pace with the supply of skilled personnel amid rapidly evolving models and tools.
Nevertheless, despite these and other challenges, companies continue to build AI-oriented business models and invest billions in R&D. It would appear the tech giants are prepared for a long AI marathon.
Subscribe to ForkLog’s Telegram updates: ForkLog AI — all the news from the AI world!
Рассылки ForkLog: держите руку на пульсе биткоин-индустрии!


