What is a vampire attack?


Key points
- A “vampire attack” is a strategy by a new blockchain project to rapidly lure users—and their capital—away from a more popular rival application.
- Typically, the new app mirrors the “original” in functionality but offers richer incentives funded by rewards in its own token.
- In autumn 2020 the decentralised exchange Uniswap was targeted; in January 2022, the NFT marketplace OpenSea.
What a vampire attack entails
A typical vampire attack has three components:
- Find a leading project.
- Create a lookalike using the original’s business model, architecture or code.
- Differentiate it with outsized economic incentives.
The aim is to “suck out” users and their capital from the target—some popular protocol.
The strategy emerged in decentralised finance (DeFi). The source code of DeFi applications, or most of it, is usually open. That makes it relatively easy to copy and launch a similar application with only minor tweaks.
Developers of the “copy” can also readily issue their own governance tokens and use them to inflate yields from liquidity farming, a standard way for users to earn.
How Uniswap became a victim of a vampire attack
In 2020, the decentralised exchange Uniswap surged in popularity across DeFi. By early September 2020, daily trading volume on the protocol reached $1.8bn, comparable with leading centralised crypto exchanges.
Against this backdrop, a project called SushiSwap appeared. Its anonymous creators did not hide that the new protocol was a fork of Uniswap. But SushiSwap had a crucial distinction—its own SUSHI token, awarded to users for farming in pools.
Whereas today a governance token is commonplace for decentralised exchanges, at the time it was far from standard practice. Even so, DeFi already had examples of their effectiveness as economic incentives.
The SushiSwap team offered enticing terms for liquidity providers: thanks to SUSHI rewards, participating in its pools delivered annual returns in the hundreds or even thousands of percent. In the course of the vampire attack, Uniswap users moved more than $1bn to SushiSwap within a couple of weeks, reducing total value locked (TVL) in the original by 70%.
The situation did not last: the rapid rate of SUSHI farming drove sharp inflation in its price, quickly compressing pool yields on SushiSwap. By mid-September Uniswap had regained the DeFi lead by TVL. Shortly afterwards the UNI governance token was launched, erasing SushiSwap’s advantage.
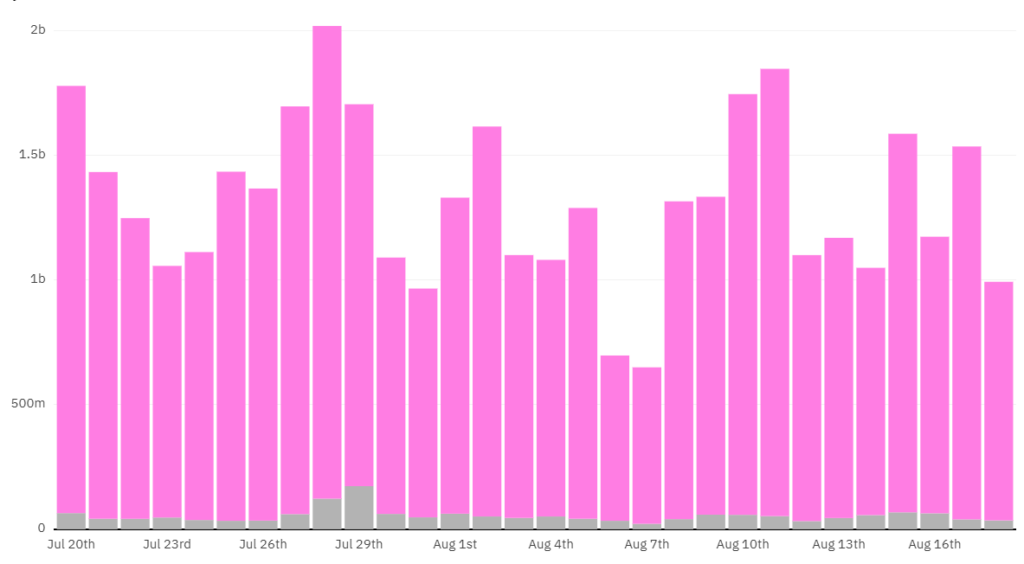
How the 2022 vampire attack on OpenSea unfolded
Another victim of the “vampires” was OpenSea, the NFT marketplace that handles the bulk of non-fungible token trading.
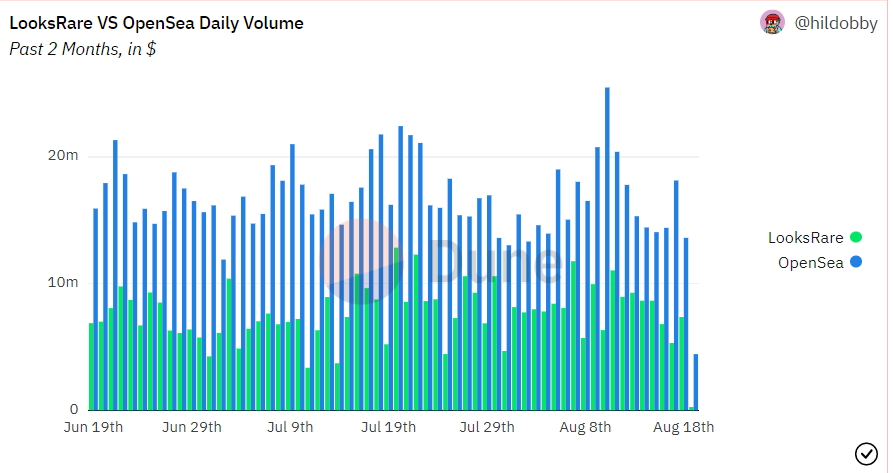
In early 2022 another platform for trading NFTs—LooksRare—went live. Although its creators, unlike SushiSwap’s, did not copy OpenSea’s smart contracts and instead wrote their own, the main element of their attack was likewise the platform token, LOOKS.
Users who traded NFTs on LooksRare received LOOKS rewards for their activity. But there was one condition: only those who had traded on OpenSea between June and December 2021 for at least 3 ETH could take part in the airdrop.
Beyond this “promotion”, users of the new platform could also earn LOOKS through staking with yields of around 500% per annum. In addition, trading fees on LooksRare were more favourable. The vampire attack led to a rapid rise in trading volumes on LooksRare and a decline on OpenSea.
LooksRare, however, lagged far behind in active users. Given the comparable trading volumes, researchers suggested that the platform’s small user base was heavily engaged in wash trading—in other words, a huge number of fake deals to earn LOOKS rewards. According to a CryptoSlam report, by early April the share of sham transactions in LooksRare’s total trading volume had reached 95%.
The platform subsequently changed incentives and began to clamp down on the practice, which curbed activity. According to The Block, turnover fell from $69m on May 1st 2022 to just $1m on August 15th, while the share of fake trades over the same period dropped from 98% to 13%. Meanwhile, OpenSea regained its leadership of the NFT market.
Notably, in 2021 the marketplace had already been subjected to a vampire attack from the Infinity platform.
Further reading
What is a decentralised exchange (DEX)?
Рассылки ForkLog: держите руку на пульсе биткоин-индустрии!


