What are rollups, and how do they scale Ethereum?

Key points
- Rollups are the core technology behind Ethereum layer-2 protocols. Many rollup designs use zero-knowledge proofs; these are grouped as ZK-rollups.
- Rollups enhance transaction privacy and scale Ethereum’s base layer: many transactions are bundled into a single batch that is verified on layer 1.
- Popular ZK-based L2s in the Ethereum ecosystem include StarkNet, zkSync, Loopring, Polygon Miden and others. A separate approach, Optimistic Rollups, is used by L2 platforms Arbitrum One and Optimism.
How do zero-knowledge proofs work?
The concept of zero-knowledge proofs (ZKP) was formulated by Shafi Goldwasser and Silvio Micali in 1985 in the paper “The Knowledge Complexity Of Interactive Proof Systems”. They proposed a way to prove a statement’s validity without revealing its details.
To do this, a special “proof” is generated that lets a verifier confirm the correctness of the underlying data. The sender performs computations that will only be correct if they possess the required knowledge. The verifier knows the value of the correct answer, enabling them to confirm possession of the information. Thus, both parties have only limited knowledge of the message’s content.
Consider a demonstration in which a colour-blind person, unable to distinguish colours, is shown two balls—one red and the other green—but they see no difference.
You must prove otherwise without naming the colours. You hand the balls to your counterpart, who hides them behind their back, then shows you one ball. They hide it again and repeat. You must answer whether they switched the ball behind their back. Since you know the correct answer, after several trials you will prove your point—without disclosing any additional information.
How are zero-knowledge proofs used in ZK-rollups?
ZKPs enabled a family of technologies known as ZK-rollups, on which many key layer-2 protocols in the Ethereum ecosystem now run. Vitalik Buterin has called ZKP the most important technology for scaling the main blockchain platform.
In a rollup (from “roll up”), batches of many transactions are formed, with each transfer’s data compressed. These bundles submit a proof to the layer‑1 network (in this case, Ethereum) that attests to the validity of all transactions in the batch without checking each one individually. After verification, the batch is included in a block. A single rollup batch can contain thousands of transactions, yet only a minimal amount of data is posted to layer 1.
ZK-rollups are powered by three components:
- an L2 virtual machine that groups transactions;
- a verifier smart contract that checks batches;
- a module that submits batches to layer 1 and updates the state.
An L2 node performs basic checks on incoming transactions. After gathering a certain number of transfers, it bundles them and generates a ZK proof. A smart contract deployed on layer 1 verifies the batch. It also handles deposits to and withdrawals from the L2 chain.
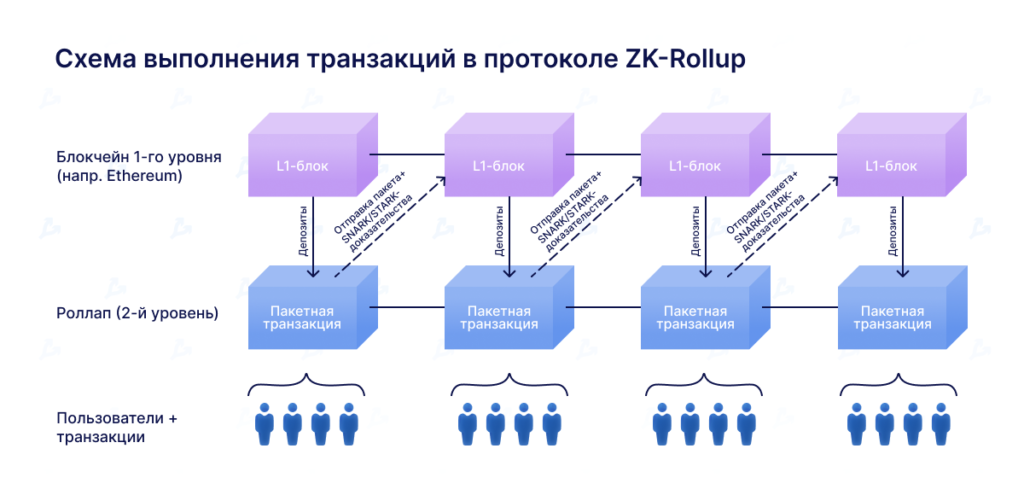
Rollups also maintain user balances in the L2 network as a Merkle tree. Its root is stored in the contract, which allows state changes to be tracked. Values confirming each transaction are also posted to layer 1. The data include the Merkle root, computed in several steps. Intermediate values are written to the blockchain and confirm every transfer in the batch.
What are the advantages of ZK-rollups?
Zero-knowledge proofs were first used in privacy coins, but in recent years they have gained wide use as scaling solutions for Ethereum.
ZK-rollups let user data be processed without revealing private information. For example, an algorithm can check that funds exist without showing a user’s balance. These properties are important for firms that must protect clients’ personal data.
Using ZK-rollup solutions also markedly reduces transaction fees. Many transfers are combined into one batch, with data compressed—for example, an index may replace an address. Less information is posted to layer 1. Costs are shared across all senders, so each user pays less.
ZK-rollups offer low withdrawal latency to the base layer because the smart contract verifies data before including the batch on-chain.
What types of ZK proofs exist?
There are many ZK-rollup implementations; the most popular include ZK-SNARKs (and the Plonky2 variant), ZK-STARKs, zkSync and others. Each differs in proof size and the computation required to verify it.
ZK-SNARK
ZK-SNARKs produce proofs that are small and easy to verify. They rely on elliptic curves. Computing their values costs less than hashing, so the algorithm is cheaper. The method requires the proof to be destroyed immediately after it is sent. For the algorithm to work, a node generates a public and a private key, after which the latter is destroyed. The public key is used to create another key pair. The private key is then used to generate the proof, and the public one to verify it.
ZK-STARK
ZK-STARKs produce a proof that does not require interaction between prover and verifier. Data validation takes less time, making the technology easier to scale. The algorithm uses hashing, which makes it resistant to quantum-computer attacks.
zkSync
zkSync is an L2 protocol based on a rollup algorithm of the same name. The platform supports asset transfers and smart contracts. A feature of the algorithm is a low gas limit per transaction that does not exceed 500 Gwei. The main advantage of zkSync 2.0 is compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine.
Which projects use ZK-rollups and Optimistic Rollups?
Several popular solutions in the Ethereum ecosystem use ZKPs:
- The StarkNet platform. Its private version, StarkEx, underpins major DeFi protocols Rhino, Immutable X, dYdX and Sorare.
- Mina Protocol is a lightweight blockchain using ZK-SNARK technology to create 22 KB blocks. The platform supports smart contracts and decentralized applications.
- LoopRing is a decentralized trading protocol that uses an order book. It is implemented on Ethereum and uses ZK proofs.
- Polygon Miden is a rollup based on zk-STARKs that operates via a dedicated virtual machine, Miden VM.
Alongside ZKP-based rollups there is a separate group known as Optimistic Rollups. The difference lies in how transactions are checked: in Optimistic systems, batches are assumed valid, and transactions are verified only if someone challenges them.
Zero-knowledge proofs persist data on the base layer after each transfer is validated, preserving the up-to-date state of the network. By contrast, withdrawing funds from an Optimistic Rollup requires a fraud check that can take up to two weeks; this determines the time to withdraw to layer 1. However, the need to verify data in ZK-rollups raises resource consumption and financial costs.
Two popular Ethereum L2 protocols run on Optimistic Rollups — Arbitrum and Optimism.
| Name | Technology used | Total value locked (TVL) |
| Polygon | Polygon Miden (ZK-STARK), Polygon Nightfall (Optimistic Rollups), Polygon Zero (Plonky2), Polygon Hermez (ZK-SNARK) | $1.3bn |
| Arbitrum One | Optimistic Rollups | $1.06bn |
| Optimism | Optimistic Rollups | $993m |
| LoopRing | ZK-SNARK | $128m |
| zkSync | zkSync | $63.76m |
| dYdX | ZK-STARK (StarkEx) | $372m |
| Aztec | PLONK (ZK-SNARK) | $11.9m |
| StarkNet | zk-STARK | $2.86m (excluding projects on StarkEx) |
What is validium?
There are composite solutions called validiums. This is a compromise technology that combines proofs and data stored at different layers. Proofs are sent to the base blockchain, while data are kept off-chain. The approach lowers fees but introduces dependence on external storage. If that storage fails, users will not lose funds but will be unable to transact.
Рассылки ForkLog: держите руку на пульсе биткоин-индустрии!


