Ethereum’s move to Proof-of-Stake (PoS): what you need to know

Key points
- Ethereum is slated for a major upgrade called The Merge, switching its consensus mechanism from Proof-of-Work (PoW) to Proof-of-Stake (PoS). The aim is to make the blockchain more scalable, secure and decentralised.
- The upgrade will unfold in two phases. It began with the successful Bellatrix update on 6 September 2022. Activation of The Merge, which implements PoS, is expected around 15 September.
- After Ethereum moves to PoS, miners will be replaced by validators. They will confirm new transactions by staking and earn rewards in ether (ETH). Current ETH staking yields stand at 4–4.5%.
- Following PoS, the next major upgrades will be the introduction of sharding and a new virtual machine supporting multiple languages for smart contracts.
When Ethereum switches to Proof-of-Stake (PoS)
According to the hard-fork schedule, it starts with the Bellatrix upgrade on 6 September, with activation of The Merge expected around 15 September. In June 2022 developers successfully integrated PoS into the Ropsten and Sepolia test networks. In early August the team executed the merge for the Goerli testnet. The Bellatrix upgrade was activated as scheduled on 6 September.
The Merge began with the launch of a network separate from mainnet called the Beacon Chain (“beacon chain”). It was there, at the end of 2020, that developers deployed a special smart contract for ETH staking, to which funds could be sent. The forthcoming upgrade is effectively a merger of the Beacon Chain and the Ethereum mainnet.
After the hard fork, Ethereum’s mainnet will be the “beacon” blockchain. Ledger data and funds in the deposit contract will be unchanged. As of 29 August 2022, the Beacon Chain has more than 420,000 validators with over 13.47m ETH staked. The Beacon Chain already uses PoS, but for now does not process transactions or smart contracts.
When staked ETH can be withdrawn
Since 2020, sending ETH to the Beacon Chain staking contract has required locking funds until The Merge is activated. Withdrawals will remain unavailable for a further 6–12 months after the upgrade concludes. At the same time, validators will start receiving liquid ETH as rewards immediately after activation of the upgrade in September 2022.
Why Ethereum is changing its consensus algorithm
Blocks in Ethereum are currently created using Proof-of-Work. This entails significant energy consumption and limits scalability. Mining also demands specialised hardware, restricting access. The upgrade is meant to address these issues and move Ethereum closer to solving the blockchain trilemma.
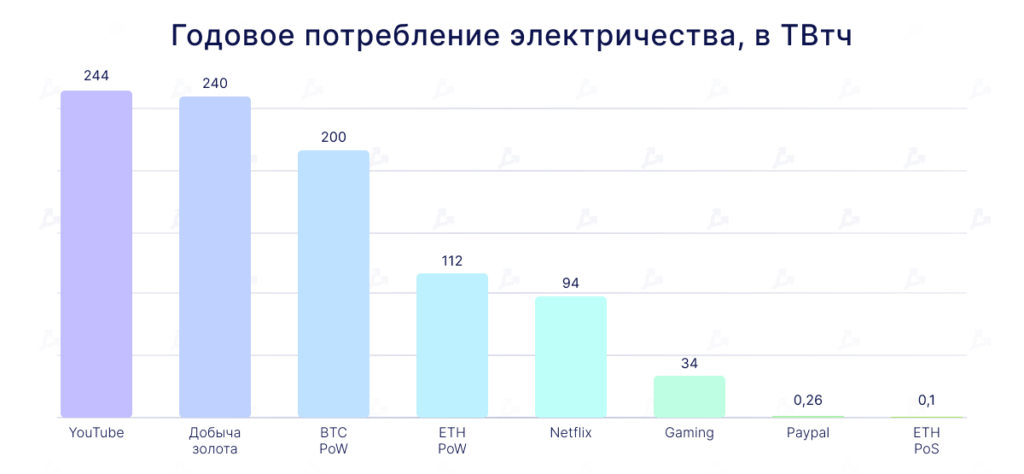
As of June 2022, Ethereum’s energy use is 112 TWh per year. Replacing mining with staking is expected to cut this by 99.95%. Developers say that on PoS, a node will consume no more electricity than a typical PC.
Another benefit is enhanced security: Ethereum should be better able to fend off attacks. The new consensus mechanism requires a large amount of capital to be locked, making it vanishingly unlikely that attackers can amass the minimum needed to compromise the network.
There is also a technical imperative. Without changing the algorithm, future upgrades to improve Ethereum’s scalability are not possible.
How PoS will work in Ethereum
In Proof-of-Stake, a validator’s voting power depends on the amount of coins committed to staking. The size of the locked stake determines a node’s rewards. To become an Ethereum validator, one must deposit at least 32 ETH into the contract. Any holder can delegate smaller amounts to a validator.
For computational efficiency, stakers are divided into randomly selected groups—committees—each comprising between 128 and 2,048 validators. Committees can be combined to create blocks.
In the upgraded Ethereum, consensus proceeds in “epochs” of roughly 6.4 minutes. Each epoch is split into 32 twelve‑second slots, during which one block is created. Committees are assigned to slots and build the chain.
A chosen validator proposes a block; the others vote on it. If it secures a majority, the block is added to the chain. After each epoch, committee membership is reshuffled. The maximum number of groups and their size are bounded by Ethereum’s supply cap of 134.2m ETH.
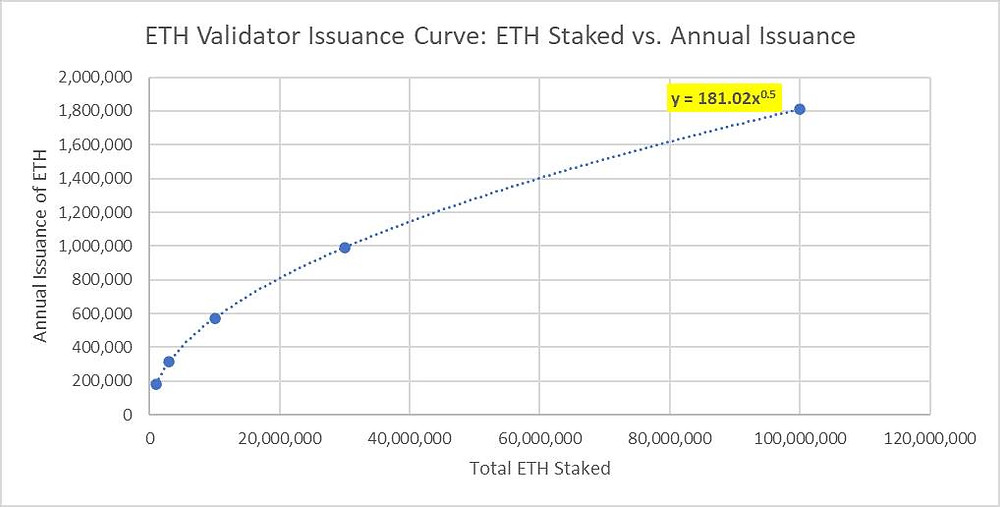
What ETH staking might yield
Ethereum fees have two parts: a priority fee and a base fee that is burned. After the switch to Proof-of-Stake, there will be no fixed block reward. Validator income will come from additional ETH issuance that adjusts dynamically each epoch. Annual issuance will depend on the total amount staked.
According to Staking Rewards at end‑August 2022, Beacon Chain validators are earning about 4.5% annually, while delegators receive roughly 4% a year. Analysts at Nansen found that more than 60% of staked ETH is controlled by just four platforms:
- Binance;
- Coinbase;
- Kraken;
- Lido Finance.
Messari analyst Tom Dunleavy suggests that immediately after the merge, ETH staking yields could rise to 7–13% annually, before trending lower over time.
How ETH’s price might react to PoS
Traders are sceptical about ETH extending its rally after the price neared the $2,000 resistance level, which Ethereum touched on 14 August. SkyBridge Capital’s Anthony Scaramucci believes ETH could rise further, but over the long term.
Most experts agree that The Merge will have a substantial impact on the crypto market.
Glassnode data suggest derivatives traders on Ethereum are “extremely optimistic” about ETH in September 2022. Based on call/put ratios and open interest, investors are betting on prices above $2,200—up to $5,000. Former BitMEX chief Arthur Hayes forecasts ETH at $3,000.
Researchers at Chainalysis note that after The Merge, Ethereum’s price could decouple from the broader crypto market.
After the move to PoS, Ethereum will retain its deflationary burn mechanism, which should also support ETH. Another potential tailwind is greater institutional adoption of Ethereum; Bank of America has flagged the possibility. Chainalysis finds that the number of ETH held by “whales” has already increased.
What happens to ETH miners—and will there be an Ethereum PoW fork?
The Merge will render Ethereum mining impossible owing to the difficulty bomb. At least some miners may migrate to another project—Ethereum Classic (ETC). It is a long‑standing fork of Ethereum and architecturally very close to its “parent”, but with a far lower hashrate and activity.
Another candidate for Ethereum miners is Ravencoin (RVN), whose price in the first two weeks of September rose by more than 100%.
A small part of the Ethereum community plans to launch a fork that preserves PoW. The initiative comes from miners and makers of specialised hardware. According to Chandler Guo’s proposal, the project could be called Ethereum PoW (ETHW).
On 13 September, ETHW developers revealed details. The fork’s mainnet is to launch within 24 hours after The Merge activates. The exact time will be announced one hour before ETHW’s mainnet goes live.
Investors are not backing the project. By mid‑September 2022, the ETHW futures price had already fallen to $30. Several large projects have declined to support an Ethereum PoW fork, including Uniswap, Chainlink, Ethermine and OpenSea.
ETH holders are likely to receive an airdrop of the ETHW fork’s coins. Binance and Bybit have said they are ready to distribute the free tokens. A similar case occurred in 2017 when Bitcoin Cash split from Bitcoin after a hard fork.
What comes after The Merge
Ethereum’s roadmap includes a technology called sharding to increase scalability. Sharding splits the database into fragments, distributing storage across nodes. This will allow Ethereum to scale with demand despite a sharp increase in ledger size.
The Beacon Chain coordinates validators and their distribution across shards. The algorithm synchronises segments so they remain aware of the network’s current state. Nodes on the upgraded mainnet will store only part of the blockchain and use specialised algorithms to verify data integrity.
Sharding will lower hardware requirements and make it possible to run a node on laptops and smartphones. The update is planned for 2023, though the final date depends on how smoothly the PoS transition proceeds.
The next step after sharding is deploying a new virtual machine, Ethereum WebAssembly (eWASM). It will enable multiple programming languages for smart contracts. eWASM is designed to make Ethereum more efficient and is expected to replace the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) over time.
What else to read
Рассылки ForkLog: держите руку на пульсе биткоин-индустрии!


